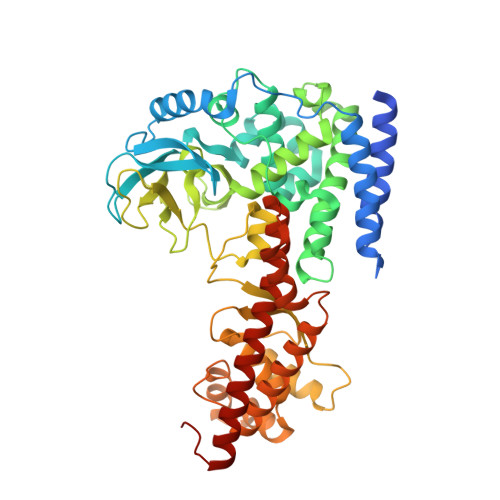
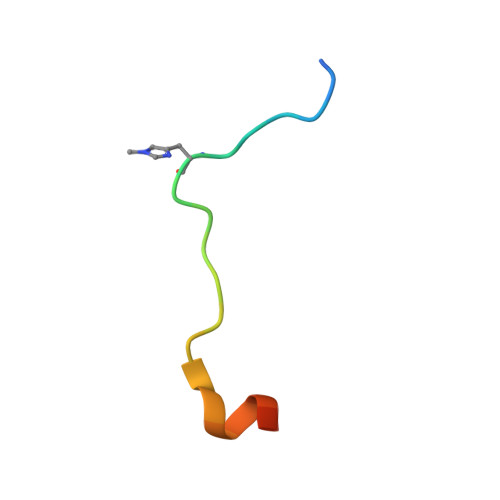
Structural insights into SETD3-mediated histidine methylation on beta-actin.
Guo, Q., Liao, S., Kwiatkowski, S., Tomaka, W., Yu, H., Wu, G., Tu, X., Min, J., Drozak, J., Xu, C.(2019) Elife 8
- PubMed: 30785395
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43676
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ICT, 6ICV - PubMed Abstract:
SETD3 is a member of the SET (Su(var)3-9, Enhancer of zeste, and Trithorax) domain protein superfamily and plays important roles in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, muscle differentiation, and carcinogenesis. Previously, we identified SETD3 as the actin-specific methyltransferase that methylates the N3 of His73 on β-actin (Kwiatkowski et al., 2018). Here, we present two structures of S -adenosyl-L-homocysteine-bound SETD3 in complex with either an unmodified β-actin peptide or its His-methylated variant. Structural analyses, supported by biochemical experiments and enzyme activity assays, indicate that the recognition and methylation of β-actin by SETD3 are highly sequence specific, and that both SETD3 and β-actin adopt pronounced conformational changes upon binding to each other. In conclusion, this study is the first to show a catalytic mechanism of SETD3-mediated histidine methylation on β-actin, which not only throws light on the protein histidine methylation phenomenon but also facilitates the design of small molecule inhibitors of SETD3.
- Division of Molecular and Cellular Biophysics, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.
Organizational Affiliation: