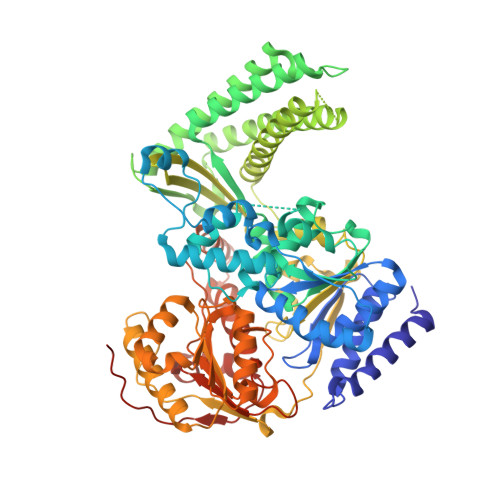
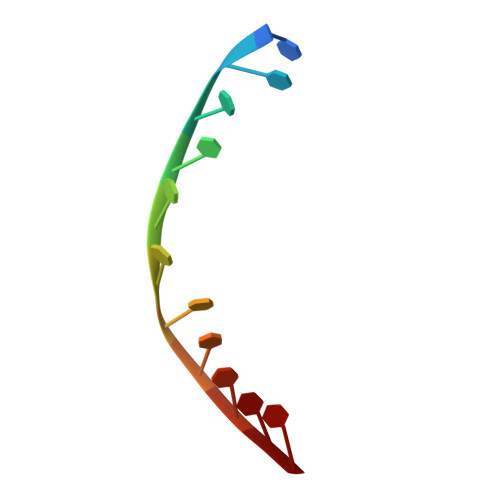
DNA translocation mechanism of an XPD family helicase.
Cheng, K., Wigley, D.B.(2018) Elife 7
- PubMed: 30520735
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42400
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FWR, 6FWS - PubMed Abstract:
The XPD family of helicases, that includes human disease-related FANCJ, DDX11 and RTEL1, are Superfamily two helicases that contain an iron-sulphur cluster domain, translocate on ssDNA in a 5'-3' direction and play important roles in genome stability. Consequently, mutations in several of these family members in eukaryotes cause human diseases. Family members in bacteria, such as the DinG helicase from Escherichia coli , are also involved in DNA repair. Here we present crystal structures of complexes of DinG bound to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in the presence and absence of an ATP analogue (ADP•BeF 3 ), that suggest a mechanism for 5'-3' translocation along the ssDNA substrate. This proposed mechanism has implications for how those enzymes of the XPD family that recognise bulky DNA lesions might stall at these as the first step in initiating DNA repair. Biochemical data reveal roles for conserved residues that are mutated in human diseases.
- Section of Structural Biology, Department of Medicine, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: