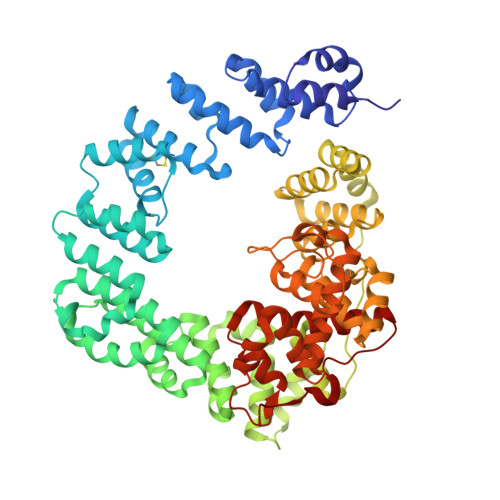
Exolytic and endolytic turnover of peptidoglycan by lytic transglycosylase Slt ofPseudomonas aeruginosa.
Lee, M., Batuecas, M.T., Tomoshige, S., Dominguez-Gil, T., Mahasenan, K.V., Dik, D.A., Hesek, D., Millan, C., Uson, I., Lastochkin, E., Hermoso, J.A., Mobashery, S.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: 4393-4398
- PubMed: 29632171
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1801298115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OHU, 6FBT, 6FC4, 6FCQ, 6FCR, 6FCS, 6FCU - PubMed Abstract:
β-Lactam antibiotics inhibit cell-wall transpeptidases, preventing the peptidoglycan, the major constituent of the bacterial cell wall, from cross-linking. This causes accumulation of long non-cross-linked strands of peptidoglycan, which leads to bacterial death. Pseudomonas aeruginosa , a nefarious bacterial pathogen, attempts to repair this aberrantly formed peptidoglycan by the function of the lytic transglycosylase Slt. We document in this report that Slt turns over the peptidoglycan by both exolytic and endolytic reactions, which cause glycosidic bond scission from a terminus or in the middle of the peptidoglycan, respectively. These reactions were characterized with complex synthetic peptidoglycan fragments that ranged in size from tetrasaccharides to octasaccharides. The X-ray structure of the wild-type apo Slt revealed it to be a doughnut-shaped protein. In a series of six additional X-ray crystal structures, we provide insights with authentic substrates into how Slt is enabled for catalysis for both the endolytic and exolytic reactions. The substrate for the exolytic reaction binds Slt in a canonical arrangement and reveals how both the glycan chain and the peptide stems are recognized by the Slt. We document that the apo enzyme does not have a fully formed active site for the endolytic reaction. However, binding of the peptidoglycan at the existing subsites within the catalytic domain causes a conformational change in the protein that assembles the surface for binding of a more expansive peptidoglycan between the catalytic domain and an adjacent domain. The complexes of Slt with synthetic peptidoglycan substrates provide an unprecedented snapshot of the endolytic reaction.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN 46556.
Organizational Affiliation: