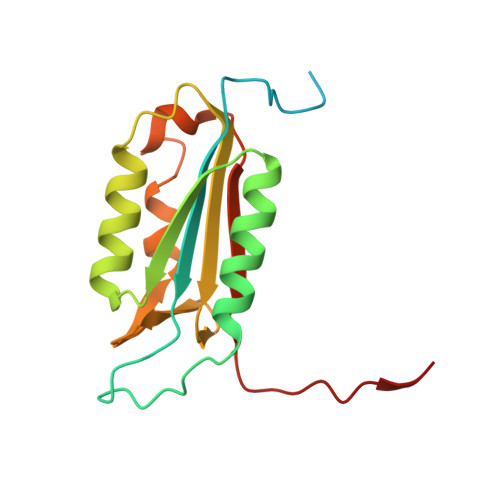
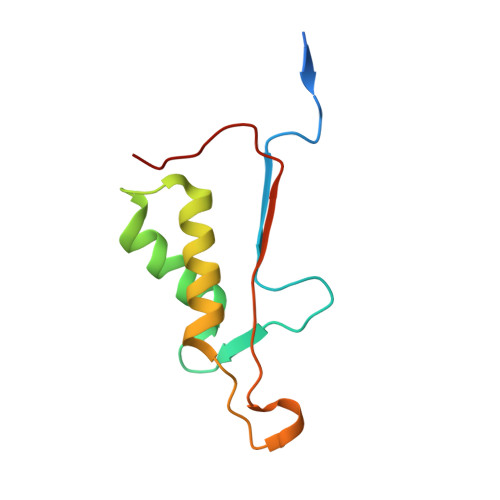
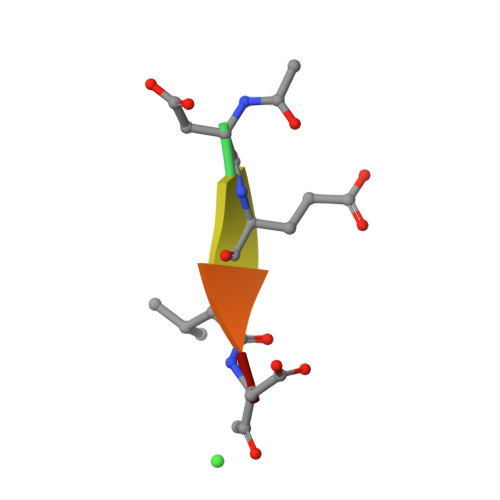
Modifications to a common phosphorylation network provide individualized control in caspases.
Thomas, M.E., Grinshpon, R., Swartz, P., Clark, A.C.(2018) J Biological Chem 293: 5447-5461
- PubMed: 29414778
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000728
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BDV, 6BFJ, 6BFK, 6BFL, 6BFO, 6BG0, 6BG1, 6BG4, 6BGK, 6BGQ, 6BGR, 6BGS, 6BH9, 6BHA - PubMed Abstract:
Caspase-3 activation and function have been well-defined during programmed cell death, but caspase activity, at low levels, is also required for developmental processes such as lymphoid proliferation and erythroid differentiation. Post-translational modification of caspase-3 is one method used by cells to fine-tune activity below the threshold required for apoptosis, but the allosteric mechanism that reduces activity is unknown. Phosphorylation of caspase-3 at a conserved allosteric site by p38-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) promotes survival in human neutrophils, and the modification of the loop is thought to be a key regulator in many developmental processes. We utilized phylogenetic, structural, and biophysical studies to define the interaction networks that facilitate the allosteric mechanism in caspase-3. We show that, within the modified loop, Ser 150 evolved with the apoptotic caspases, whereas Thr 152 is a more recent evolutionary event in mammalian caspase-3. Substitutions at Ser 150 result in a pH-dependent decrease in dimer stability, and localized changes in the modified loop propagate to the active site of the same protomer through a connecting surface helix. Likewise, a cluster of hydrophobic amino acids connects the conserved loop to the active site of the second protomer. The presence of Thr 152 in the conserved loop introduces a "kill switch" in mammalian caspase-3, whereas the more ancient Ser 150 reduces without abolishing enzyme activity. These data reveal how evolutionary changes in a conserved allosteric site result in a common pathway for lowering activity during development or a more recent cluster-specific switch to abolish activity.
- From the Department of Molecular and Structural Biochemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 27608 and.
Organizational Affiliation: