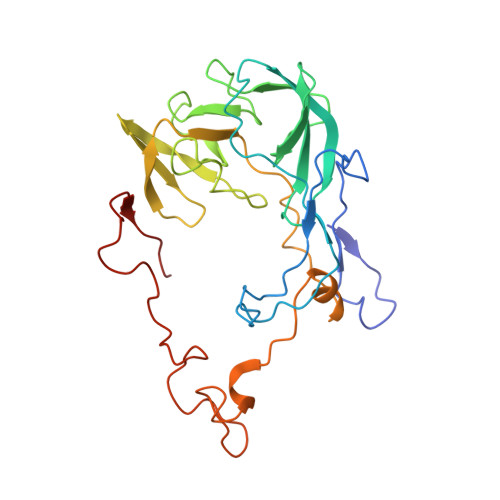
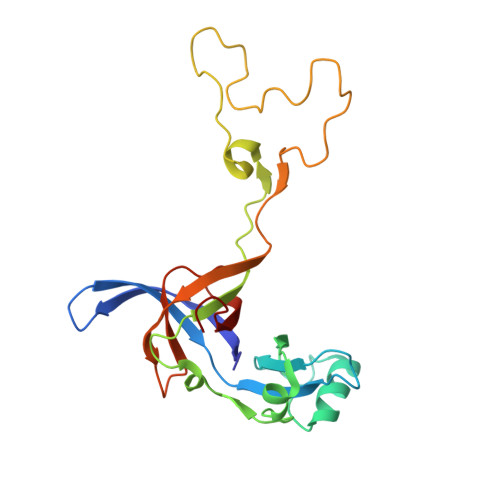
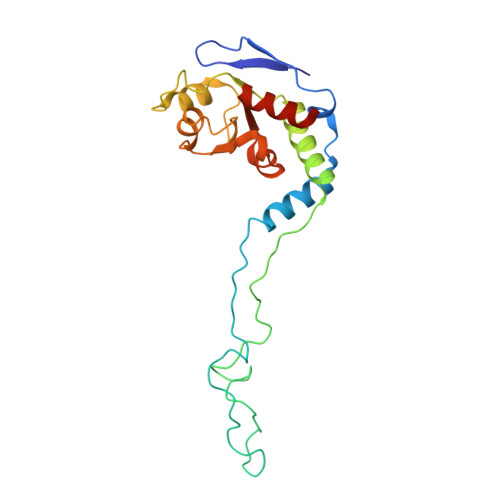
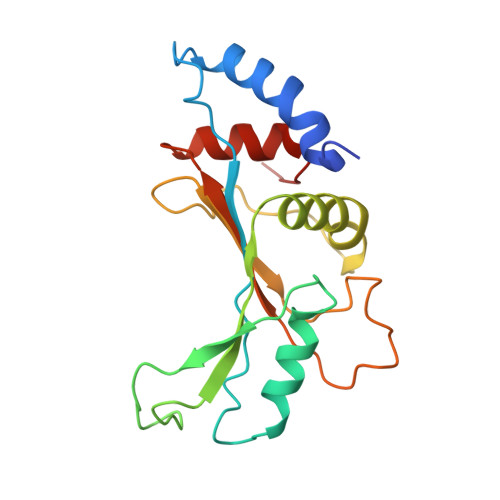
Structures of Mycobacterium smegmatis 70S ribosomes in complex with HPF, tmRNA, and P-tRNA.
Mishra, S., Ahmed, T., Tyagi, A., Shi, J., Bhushan, S.(2018) Sci Rep 8: 13587-13587
- PubMed: 30206241
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31850-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ZEB, 5ZEP, 5ZET, 5ZEU, 5ZEY - PubMed Abstract:
Ribosomes are the dynamic protein synthesis machineries of the cell. They may exist in different functional states in the cell. Therefore, it is essential to have structural information on these different functional states of ribosomes to understand their mechanism of action. Here, we present single particle cryo-EM reconstructions of the Mycobacterium smegmatis 70S ribosomes in the hibernating state (with HPF), trans-translating state (with tmRNA), and the P/P state (with P-tRNA) resolved to 4.1, 12.5, and 3.4 Å, respectively. A comparison of the P/P state with the hibernating state provides possible functional insights about the Mycobacteria-specific helix H54a rRNA segment. Interestingly, densities for all the four OB domains of bS1 protein is visible in the hibernating 70S ribosome displaying the molecular details of bS1-70S interactions. Our structural data shows a Mycobacteria-specific H54a-bS1 interaction which seems to prevent subunit dissociation and degradation during hibernation without the formation of 100S dimer. This indicates a new role of bS1 protein in 70S protection during hibernation in Mycobacteria in addition to its conserved function during translation initiation.
- School of Biological Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: