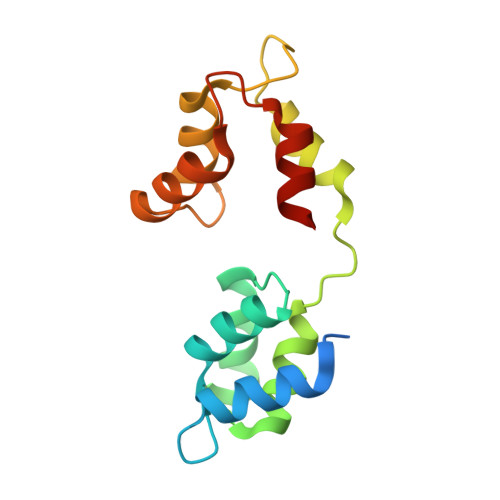
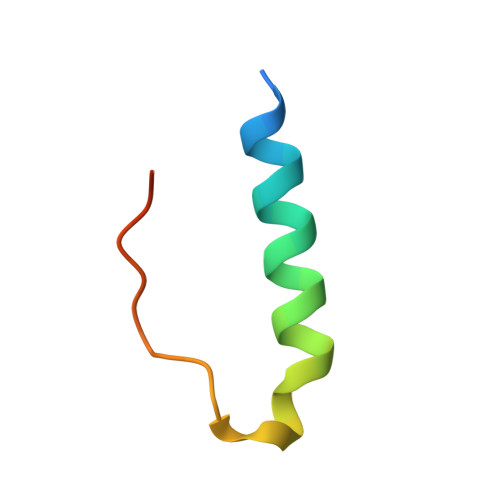
Dissecting the molecular assembly of the Toxoplasma gondii MyoA motility complex.
Powell, C.J., Jenkins, M.L., Parker, M.L., Ramaswamy, R., Kelsen, A., Warshaw, D.M., Ward, G.E., Burke, J.E., Boulanger, M.J.(2017) J Biological Chem 292: 19469-19477
- PubMed: 28972141
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.809632
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VT9 - PubMed Abstract:
Apicomplexan parasites such as Toxoplasma gondii rely on a unique form of locomotion known as gliding motility. Generating the mechanical forces to support motility are divergent class XIV myosins (MyoA) coordinated by accessory proteins known as light chains. Although the importance of the MyoA-light chain complex is well-established, the detailed mechanisms governing its assembly and regulation are relatively unknown. To establish a molecular blueprint of this dynamic complex, we first mapped the adjacent binding sites of light chains MLC1 and ELC1 on the MyoA neck (residues 775-818) using a combination of hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry and isothermal titration calorimetry. We then determined the 1.85 Å resolution crystal structure of MLC1 in complex with its cognate MyoA peptide. Structural analysis revealed a bilobed architecture with MLC1 clamping tightly around the helical MyoA peptide, consistent with the stable 10 nm K d measured by isothermal titration calorimetry. We next showed that coordination of calcium by an EF-hand in ELC1 and prebinding of MLC1 to the MyoA neck enhanced the affinity of ELC1 for the MyoA neck 7- and 8-fold, respectively. When combined, these factors enhanced ELC1 binding 49-fold (to a K d of 12 nm). Using the full-length MyoA motor (residues 1-831), we then showed that, in addition to coordinating the neck region, ELC1 appears to engage the MyoA converter subdomain, which couples the motor domain to the neck. These data support an assembly model where staged binding events cooperate to yield high-affinity complexes that are able to maximize force transduction.
- From the Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia V8P 5C2, Canada and.
Organizational Affiliation: