Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 Is Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain in Response to Allosteric Effectors.
Caldo, K.M.P., Acedo, J.Z., Panigrahi, R., Vederas, J.C., Weselake, R.J., Lemieux, M.J.(2017) Plant Physiol 175: 667-680
- PubMed: 28827454
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00934
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UZL - PubMed Abstract:
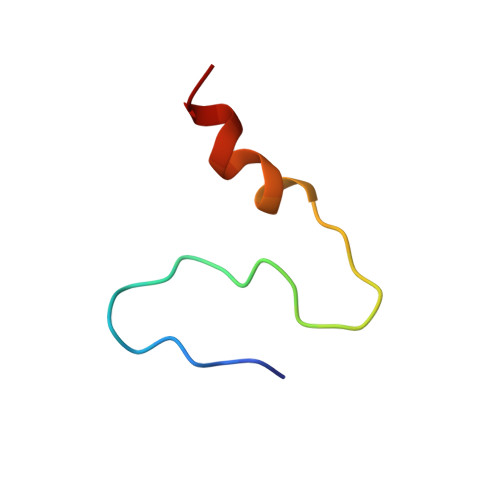
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) is an integral membrane enzyme catalyzing the final and committed step in the acyl-coenzyme A (CoA)-dependent biosynthesis of triacylglycerol (TAG). The biochemical regulation of TAG assembly remains one of the least understood areas of primary metabolism to date. Here, we report that the hydrophilic N-terminal domain of Brassica napus DGAT1 (BnaDGAT1 1-113 ) regulates activity based on acyl-CoA/CoA levels. The N-terminal domain is not necessary for acyltransferase activity and is composed of an intrinsically disordered region and a folded segment. We show that the disordered region has an autoinhibitory function and a dimerization interface, which appears to mediate positive cooperativity, whereas the folded segment of the cytosolic region was found to have an allosteric site for acyl-CoA/CoA. Under increasing acyl-CoA levels, the binding of acyl-CoA with this noncatalytic site facilitates homotropic allosteric activation. Enzyme activation, on the other hand, is prevented under limiting acyl-CoA conditions (low acyl-CoA-to-CoA ratio), whereby CoA acts as a noncompetitive feedback inhibitor through interaction with the same folded segment. The three-dimensional NMR solution structure of the allosteric site revealed an α-helix with a loop connecting a coil fragment. The conserved amino acid residues in the loop interacting with CoA were identified, revealing details of this important regulatory element for allosteric regulation. Based on these results, a model is proposed illustrating the role of the N-terminal domain of BnaDGAT1 as a positive and negative modulator of TAG biosynthesis.
- Department of Agricultural, Food, and Nutritional Science, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2P5, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: