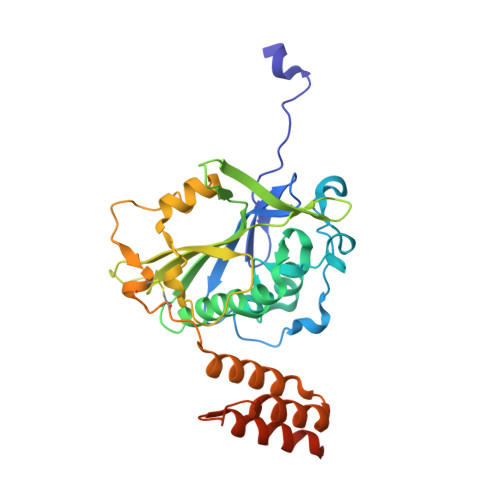
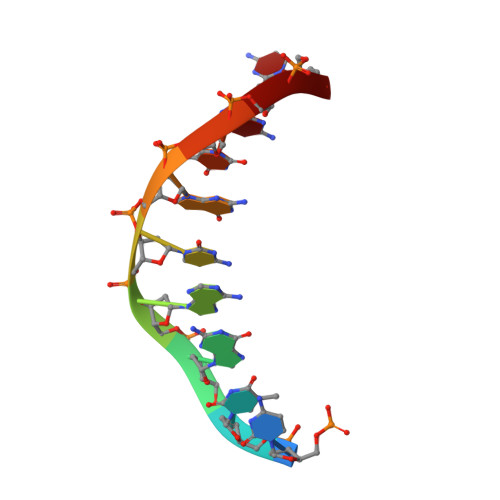
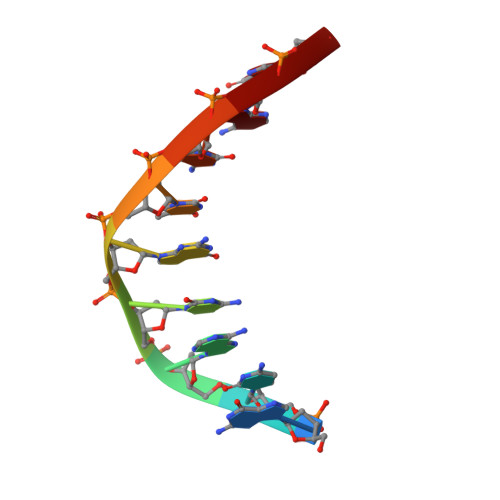
A domain in human EXOG converts apoptotic endonuclease to DNA-repair exonuclease.
Szymanski, M.R., Yu, W., Gmyrek, A.M., White, M.A., Molineux, I.J., Lee, J.C., Yin, Y.W.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 14959-14959
- PubMed: 28466855
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14959
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5T3V, 5T40, 5T4I, 5T5C - PubMed Abstract:
Human EXOG (hEXOG) is a 5'-exonuclease that is crucial for mitochondrial DNA repair; the enzyme belongs to a nonspecific nuclease family that includes the apoptotic endonuclease EndoG. Here we report biochemical and structural studies of hEXOG, including structures in its apo form and in a complex with DNA at 1.81 and 1.85 Å resolution, respectively. A Wing domain, absent in other ββα-Me members, suppresses endonuclease activity, but confers on hEXOG a strong 5'-dsDNA exonuclease activity that precisely excises a dinucleotide using an intrinsic 'tape-measure'. The symmetrical apo hEXOG homodimer becomes asymmetrical upon binding to DNA, providing a structural basis for how substrate DNA bound to one active site allosterically regulates the activity of the other. These properties of hEXOG suggest a pathway for mitochondrial BER that provides an optimal substrate for subsequent gap-filling synthesis by DNA polymerase γ.
- Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas 77555, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: