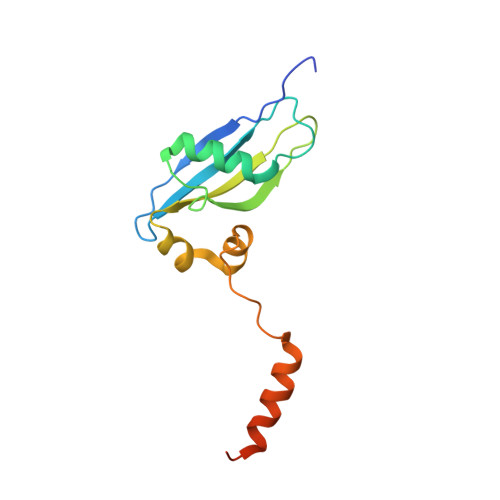
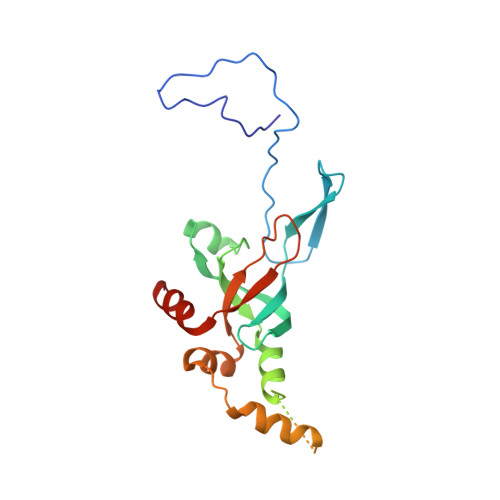
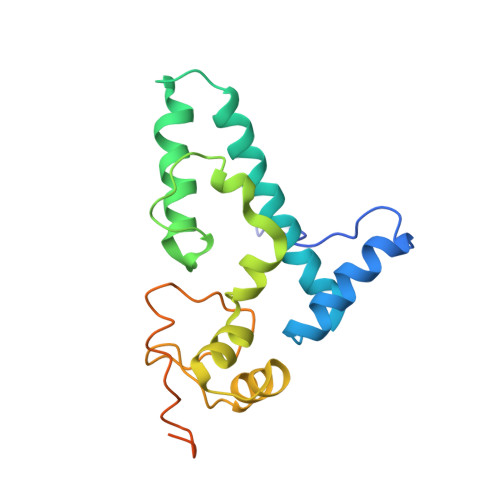
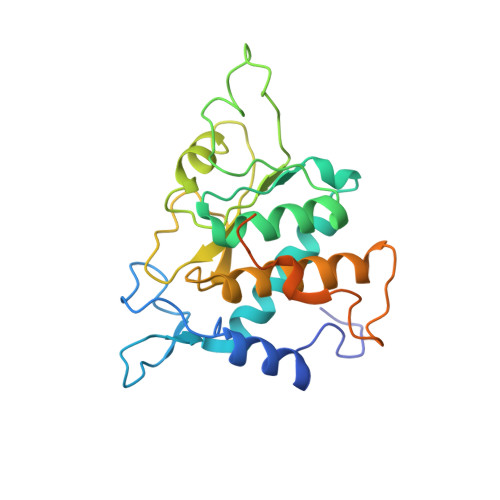
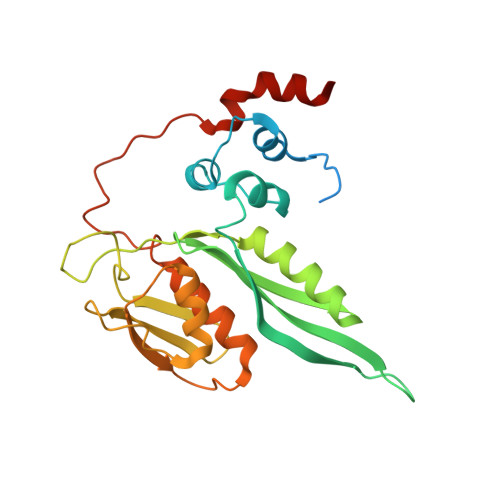
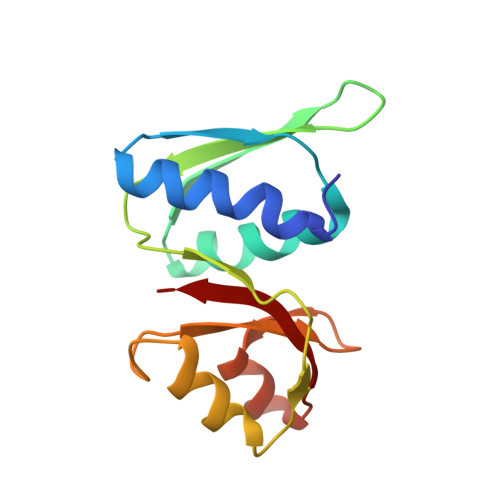
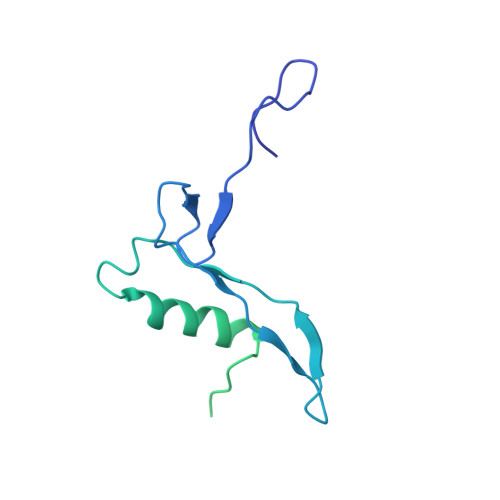
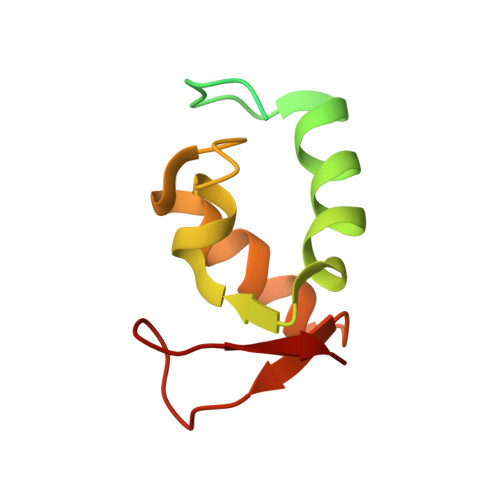
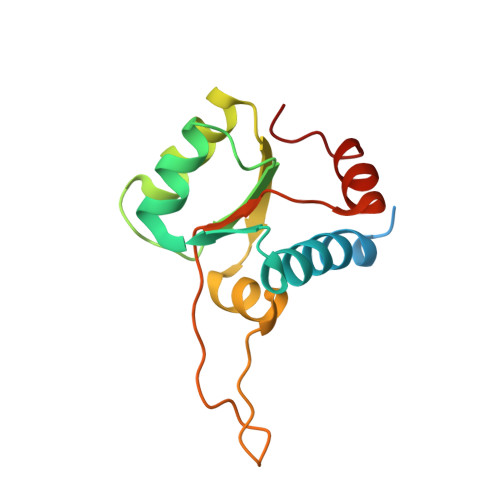
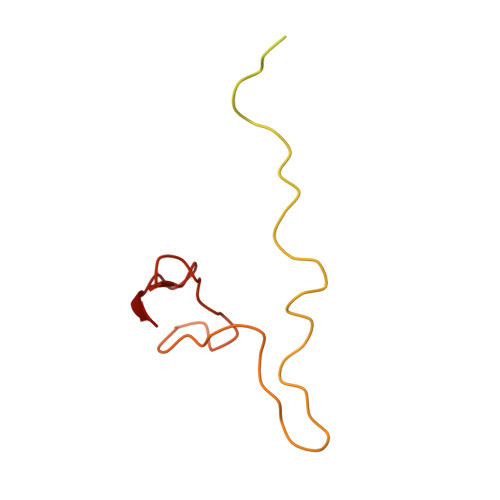
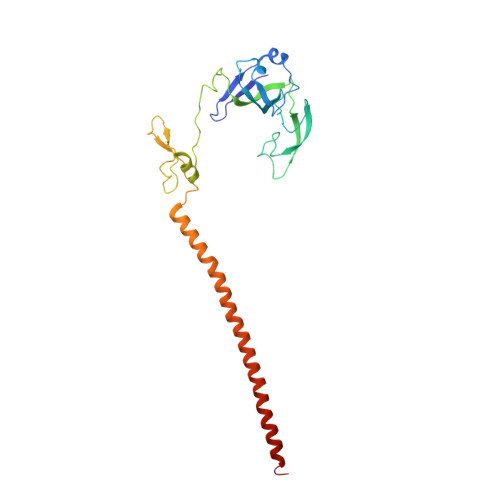
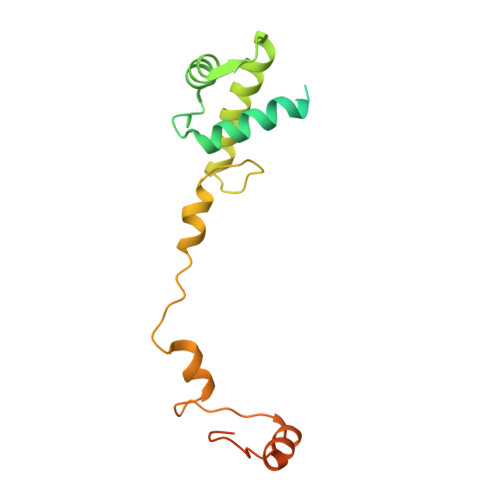
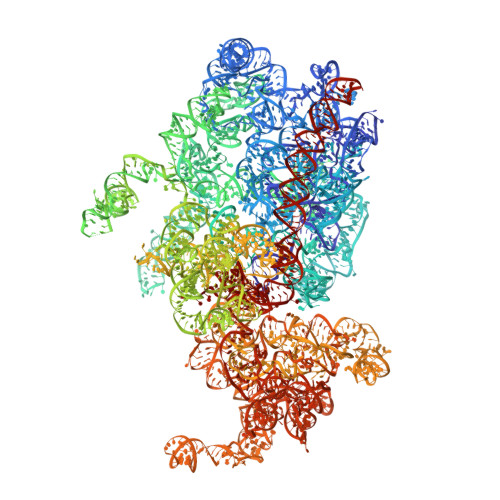
The cryo-EM Structure of a Novel 40S Kinetoplastid-Specific Ribosomal Protein.
Brito Querido, J., Mancera-Martinez, E., Vicens, Q., Bochler, A., Chicher, J., Simonetti, A., Hashem, Y.(2017) Structure 25: 1785-1794.e3
- PubMed: 29107485
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.09.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OPT, 5OSG - PubMed Abstract:
Kinetoplastids are potentially lethal protozoan pathogens affecting more than 20 million people worldwide. There is a critical need for more specific targets for the development of safer anti-kinetoplastid therapeutic molecules that can replace the scarce and highly cytotoxic current drugs. The kinetoplastid ribosome represents a potential therapeutic target due to its relative structural divergence when compared with its human counterpart. However, several kinetoplastid-specific ribosomal features remain uncharacterized. Here, we present the near-atomic cryoelectron microscopy structure of a novel bona fide kinetoplastid-specific ribosomal (r-) protein (KSRP) bound to the ribosome. KSRP is an essential protein located at the solvent face of the 40S subunit, where it binds and stabilizes kinetoplastid-specific domains of rRNA, suggesting its role in ribosome integrity. KSRP also interacts with the r-protein eS6 at a region that is only conserved in kinetoplastids. The kinetoplastid-specific ribosomal environment of KSRP provides a promising target for the design of safer anti-kinetoplastidian drugs.
- Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, Architecture et Réactivité de l'ARN, UPR 9002, 67000 Strasbourg, France.
Organizational Affiliation: