Ca(2+)-induced movement of tropomyosin on native cardiac thin filaments revealed by cryoelectron microscopy.
Risi, C., Eisner, J., Belknap, B., Heeley, D.H., White, H.D., Schroder, G.F., Galkin, V.E.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: 6782-6787
- PubMed: 28607071
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700868114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NOG, 5NOJ, 5NOL - PubMed Abstract:
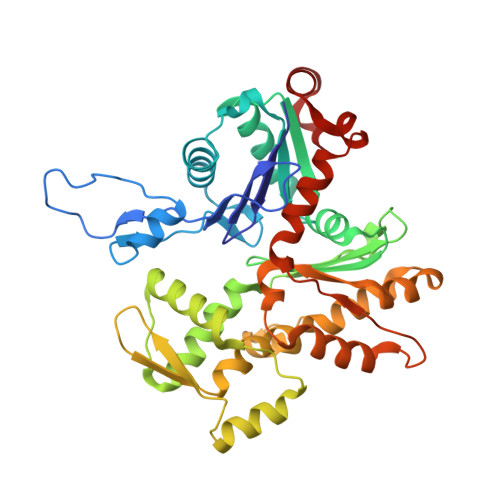
Muscle contraction relies on the interaction of myosin motors with F-actin, which is regulated through a translocation of tropomyosin by the troponin complex in response to Ca 2+ The current model of muscle regulation holds that at relaxing (low-Ca 2+ ) conditions tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites on F-actin, whereas at activating (high-Ca 2+ ) conditions tropomyosin translocation only partially exposes myosin binding sites on F-actin so that binding of rigor myosin is required to fully activate the thin filament (TF). Here we used a single-particle approach to helical reconstruction of frozen hydrated native cardiac TFs under relaxing and activating conditions to reveal the azimuthal movement of the tropomyosin on the surface of the native cardiac TF upon Ca 2+ activation. We demonstrate that at either relaxing or activating conditions tropomyosin is not constrained in one structural state, but rather is distributed between three structural positions on the surface of the TF. We show that two of these tropomyosin positions restrain actomyosin interactions, whereas in the third position, which is significantly enhanced at high Ca 2+ , tropomyosin does not block myosin binding sites on F-actin. Our data provide a structural framework for the enhanced activation of the cardiac TF over the skeletal TF by Ca 2+ and lead to a mechanistic model for the regulation of the cardiac TF.
- Department of Physiological Sciences, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA 23507.
Organizational Affiliation: