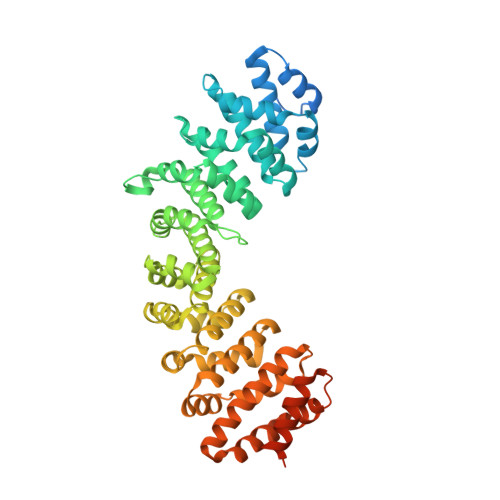
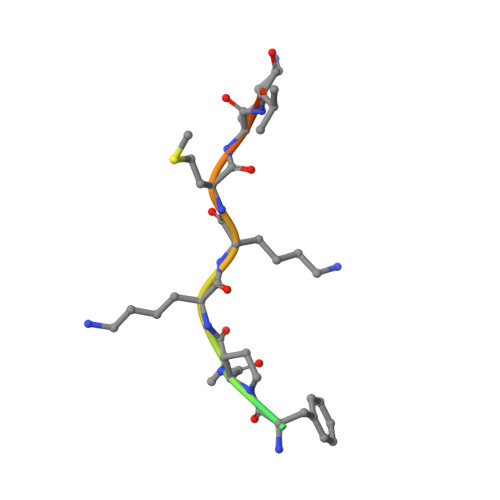
Contribution of the residue at position 4 within classical nuclear localization signals to modulating interaction with importins and nuclear targeting.
Smith, K.M., Di Antonio, V., Bellucci, L., Thomas, D.R., Caporuscio, F., Ciccarese, F., Ghassabian, H., Wagstaff, K.M., Forwood, J.K., Jans, D.A., Palu, G., Alvisi, G.(2018) Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865: 1114-1129
- PubMed: 29750988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KLR, 5KLT - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear import involves the recognition by importin (IMP) superfamily members of nuclear localization signals (NLSs) within protein cargoes destined for the nucleus, the best understood being recognition of classical NLSs (cNLSs) by the IMPα/β1 heterodimer. Although the cNLS consensus [K-(K/R)-X-(K/R) for positions P2-P5] is generally accepted, recent studies indicated that the contribution made by different residues at the P4 position can vary. Here, we apply a combination of microscopy, molecular dynamics, crystallography, in vitro binding, and bioinformatics approaches to show that the nature of residues at P4 indeed modulates cNLS function in the context of a prototypical Simian Virus 40 large tumor antigen-derived cNLS (KKRK, P2-5). Indeed, all hydrophobic substitutions in place of R impaired binding to IMPα and nuclear targeting, with the largest effect exerted by a G residue at P4. Substitution of R with neutral hydrophobic residues caused the loss of electrostatic and van der Waals interactions between the P4 residue side chains and IMPα. Detailed bioinformatics analysis confirmed the importance of the P4 residue for cNLS function across the human proteome, with specific residues such as G being associated with low activity. Furthermore, we validate our findings for two additional cNLSs from human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) DNA polymerase catalytic subunit UL54 and processivity factor UL44, where a G residue at P4 results in a 2-3-fold decrease in NLS activity. Our results thus showed that the P4 residue makes a hitherto poorly appreciated contribution to nuclear import efficiency, which is essential to determining the precise nuclear levels of cargoes.
- School of Biomedical Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales 2650, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: