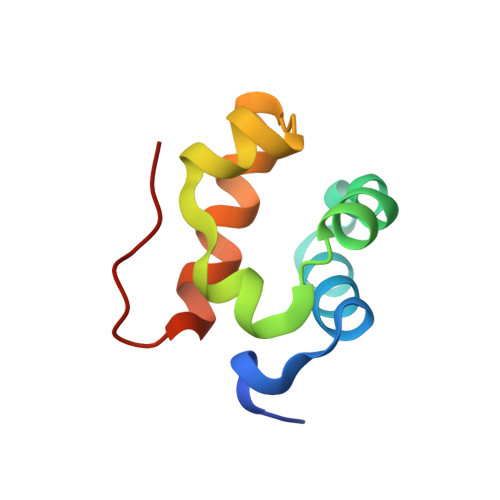
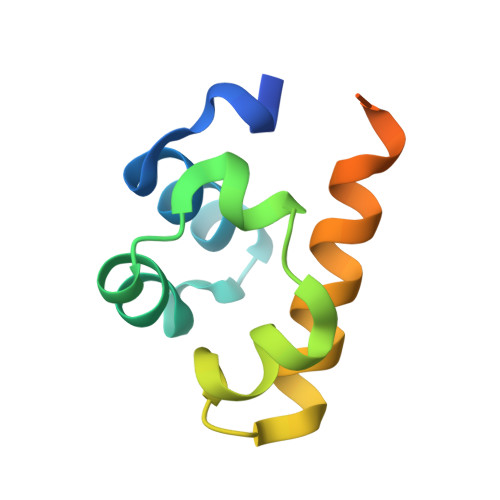
Molecular basis of PRC1 targeting to Polycomb response elements by PhoRC.
Frey, F., Sheahan, T., Finkl, K., Stoehr, G., Mann, M., Benda, C., Muller, J.(2016) Genes Dev 30: 1116-1127
- PubMed: 27151979
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.279141.116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5J8Y - PubMed Abstract:
Polycomb group (PcG) protein complexes repress transcription by modifying target gene chromatin. In Drosophila, this repression requires association of PcG protein complexes with cis-regulatory Polycomb response elements (PREs), but the interactions permitting formation of these assemblies are poorly understood. We show that the Sfmbt subunit of the DNA-binding Pho-repressive complex (PhoRC) and the Scm subunit of the canonical Polycomb-repressive complex 1 (PRC1) directly bind each other through their SAM domains. The 1.9 Å crystal structure of the Scm-SAM:Sfmbt-SAM complex reveals the recognition mechanism and shows that Sfmbt-SAM lacks the polymerization capacity of the SAM domains of Scm and its PRC1 partner subunit, Ph. Functional analyses in Drosophila demonstrate that Sfmbt-SAM and Scm-SAM are essential for repression and that PhoRC DNA binding is critical to initiate PRC1 association with PREs. Together, this suggests that PRE-tethered Sfmbt-SAM nucleates PRC1 recruitment and that Scm-SAM/Ph-SAM-mediated polymerization then results in the formation of PRC1-compacted chromatin.
- Laboratory of Chromatin Biology, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, 82152 Martinsried, Germany;
Organizational Affiliation: