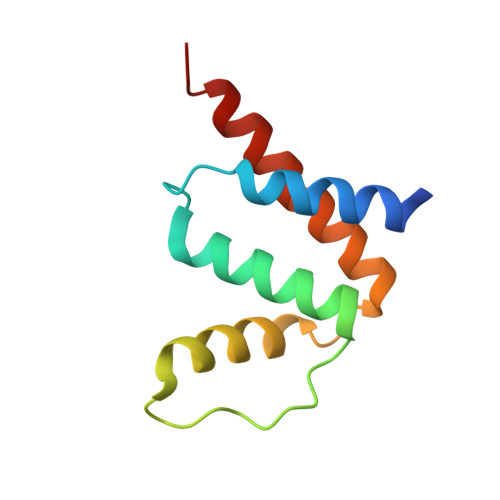
The first plant acyl-CoA-binding protein structures: the close homologues OsACBP1 and OsACBP2 from rice
Guo, Z.-H., Chan, W.H.Y., Kong, G.K.W., Hao, Q., Chye, M.-L.(2017) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 73: 438-448
- PubMed: 28471368
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798317004193
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H3G, 5H3I - PubMed Abstract:
Acyl-CoA-binding proteins (ACBPs) are a family of proteins that facilitate the binding of long-chain acyl-CoA esters at a conserved acyl-CoA-binding domain. ACBPs act to form intracellular acyl-CoA pools, transport acyl-CoA esters and regulate lipid metabolism. In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, a family of six ACBPs has been demonstrated to function in stress and development. Six ACBPs (OsACBPs) have also been identified in Oryza sativa (rice), but they are not as well characterized as those in Arabidopsis thaliana. To understand the need in rice for the two 10 kDa ACBPs, namely OsACBP1 and OsACBP2, which share 79% sequence identity, their crystal structures were elucidated and their affinities toward acyl-CoA esters were compared using isothermal titration calorimetry. OsACBP2 was found to display a higher binding affinity for unsaturated acyl-CoA esters than OsACBP1. A difference between the two proteins is observed at helix 3 and is predicted to lead to different ligand-binding modes in terms of the shape of the binding pocket and the residues that are involved. OsACBP1 thus resembles bovine ACBP, while OsACBP2 is similar to human liver ACBP, in both structure and binding affinity. This is the first time that ACBP structures have been reported from plants, and suggests that OsACBP1 and OsACBP2 are not redundant in function despite their high sequence identity and general structural similarity.
- School of Biological Sciences, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong.
Organizational Affiliation: