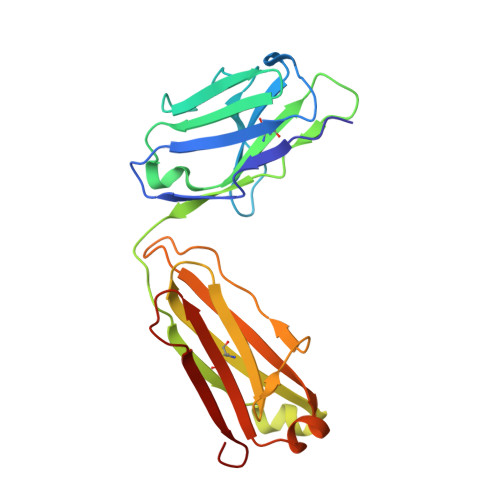
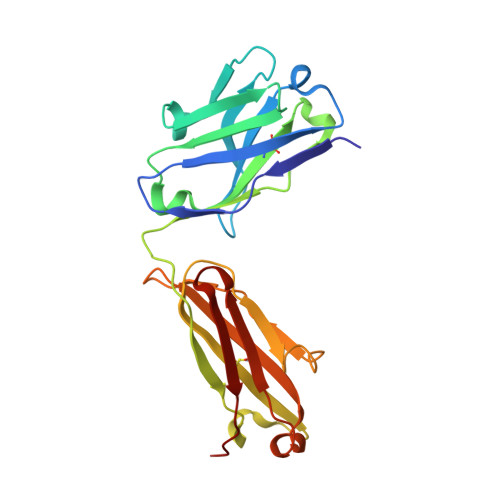
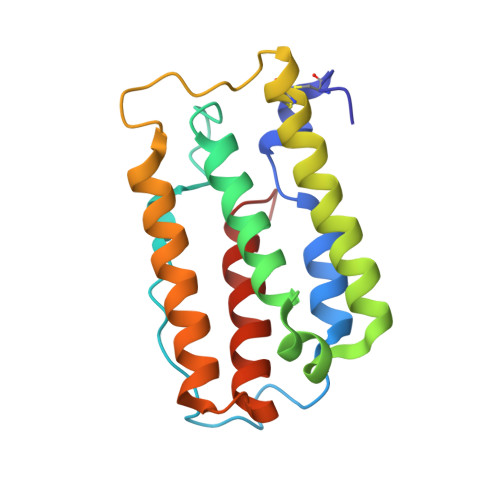
Structural Insights into the Neutralization Properties of the Fully Human, Anti-interferon Monoclonal Antibody Sifalimumab.
Oganesyan, V., Peng, L., Woods, R.M., Wu, H., Dall'Acqua, W.F.(2015) J Biological Chem 290: 14979-14985
- PubMed: 25925951
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.652156
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YPG - PubMed Abstract:
We report the three-dimensional structure of human interferon α-2A (IFN-α2A) bound to the Fab fragment of a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (sifalimumab; IgG1/κ). The structure of the corresponding complex was solved at a resolution of 3.0 Å using molecular replacement and constitutes the first reported structure of a human type I IFN bound to a therapeutic antibody. This study revealed the major contribution made by the first complementarity-determining region in each of sifalimumab light and heavy chains. These data also provided the molecular basis for sifalimumab mechanism of action. We propose that its interferon-neutralizing properties are the result of direct competition for IFN-α2A binding to the IFN receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1) and do not involve inhibiting IFN-α2A binding to the IFN receptor subunit 2 (IFNAR2).
- From the Department of Antibody Discovery and Protein Engineering, MedImmune LLC, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20878 oganesyanv@medimmune.com.
Organizational Affiliation: