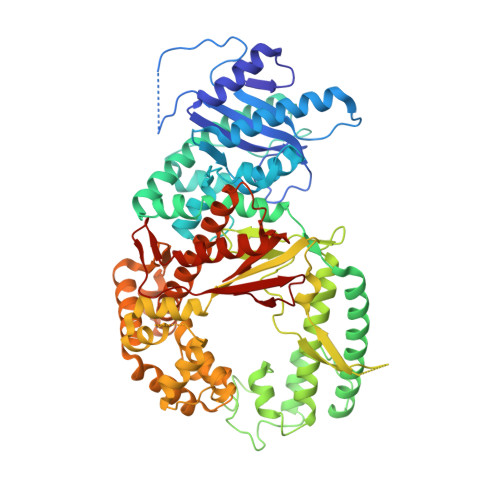
How a homolog of high-fidelity replicases conducts mutagenic DNA synthesis.
Lee, Y.S., Gao, Y., Yang, W.(2015) Nat Struct Mol Biol 22: 298-303
- PubMed: 25775266
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2985
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XVI, 4XVK, 4XVL, 4XVM - PubMed Abstract:
All DNA replicases achieve high fidelity by a conserved mechanism, but each translesion polymerase carries out mutagenic DNA synthesis in its own way. Here we report crystal structures of human DNA polymerase ν (Pol ν), which is homologous to high-fidelity replicases yet is error prone. Instead of a simple open-to-closed movement of the O helix upon binding of a correct incoming nucleotide, Pol ν has a different open state and requires the finger domain to swing sideways and undergo both opening and closing motions to accommodate the nascent base pair. A single-amino acid substitution in the O helix of the finger domain improves the fidelity of Pol ν nearly ten-fold. A unique cavity and the flexibility of the thumb domain allow Pol ν to generate and accommodate a looped-out primer strand. Primer loop-out may be a mechanism for DNA trinucloetide-repeat expansion.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: