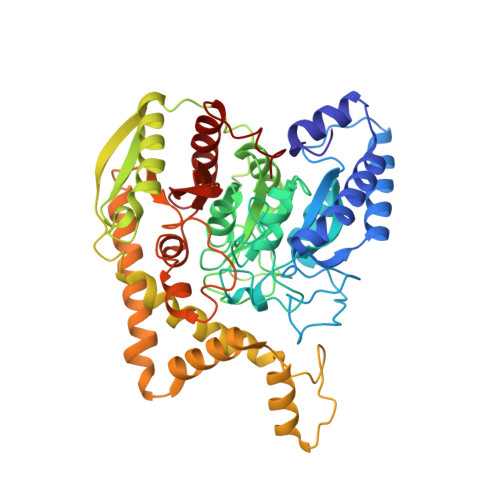
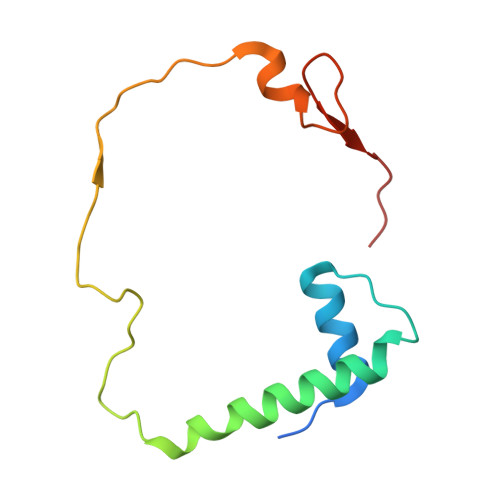
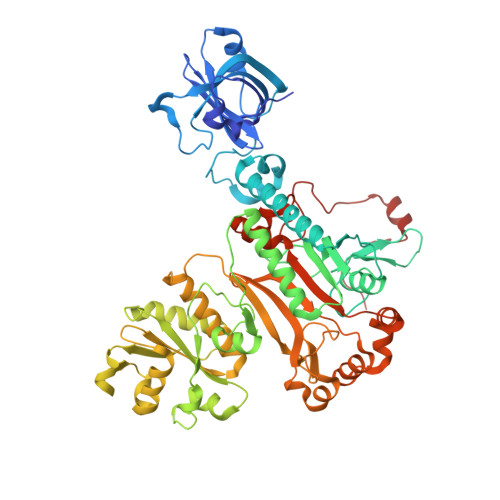
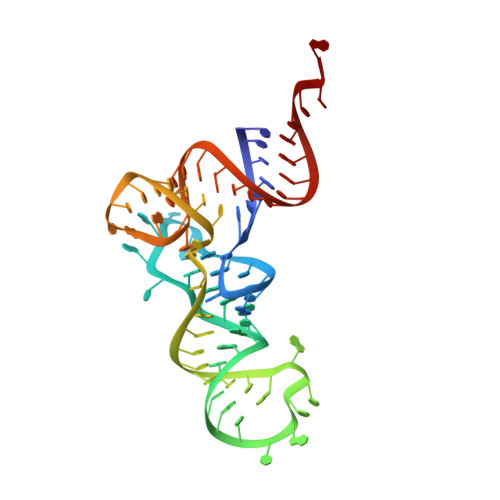
Structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa transamidosome reveals unique aspects of bacterial tRNA-dependent asparagine biosynthesis
Suzuki, T., Nakamura, A., Kato, K., Soll, D., Tanaka, I., Sheppard, K., Yao, M.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 382-387
- PubMed: 25548166
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423314112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WJ3, 4WJ4 - PubMed Abstract:
Many prokaryotes lack a tRNA synthetase to attach asparagine to its cognate tRNA(Asn), and instead synthesize asparagine from tRNA(Asn)-bound aspartate. This conversion involves two enzymes: a nondiscriminating aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (ND-AspRS) that forms Asp-tRNA(Asn), and a heterotrimeric amidotransferase GatCAB that amidates Asp-tRNA(Asn) to form Asn-tRNA(Asn) for use in protein synthesis. ND-AspRS, GatCAB, and tRNA(Asn) may assemble in an ∼400-kDa complex, known as the Asn-transamidosome, which couples the two steps of asparagine biosynthesis in space and time to yield Asn-tRNA(Asn). We report the 3.7-Å resolution crystal structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Asn-transamidosome, which represents the most common machinery for asparagine biosynthesis in bacteria. We show that, in contrast to a previously described archaeal-type transamidosome, a bacteria-specific GAD domain of ND-AspRS provokes a principally new architecture of the complex. Both tRNA(Asn) molecules in the transamidosome simultaneously serve as substrates and scaffolds for the complex assembly. This architecture rationalizes an elevated dynamic and a greater turnover of ND-AspRS within bacterial-type transamidosomes, and possibly may explain a different evolutionary pathway of GatCAB in organisms with bacterial-type vs. archaeal-type Asn-transamidosomes. Importantly, because the two-step pathway for Asn-tRNA(Asn) formation evolutionarily preceded the direct attachment of Asn to tRNA(Asn), our structure also may reflect the mechanism by which asparagine was initially added to the genetic code.
- Graduate School of Life Science and.
Organizational Affiliation: