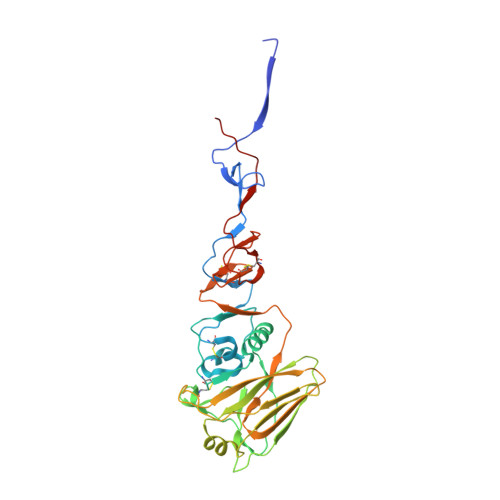
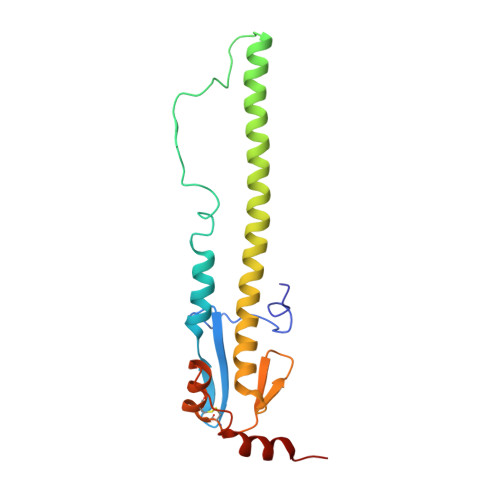
Recent Evolution of Equine Influenza and the Origin of Canine Influenza.
Collins, P.J., Vachieri, S.G., Haire, L.F., Ogrodowicz, R.W., Martin, S.R., Walker, P.A., Xiong, X., Gamblin, S.J., Skehel, J.J.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 11175
- PubMed: 25024224
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1406606111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UNW, 4UNX, 4UNY, 4UNZ, 4UO0, 4UO1, 4UO2, 4UO3, 4UO4, 4UO5, 4UO6, 4UO7, 4UO8, 4UO9, 4UOA - PubMed Abstract:
In 2004 an hemagglutinin 3 neuraminidase 8 (H3N8) equine influenza virus was transmitted from horses to dogs in Florida and subsequently spread throughout the United States and to Europe. To understand the molecular basis of changes in the antigenicity of H3 hemagglutinins (HAs) that have occurred during virus evolution in horses, and to investigate the role of HA in the equine to canine cross-species transfer, we used X-ray crystallography to determine the structures of the HAs from two antigenically distinct equine viruses and from a canine virus. Structurally all three are very similar with the majority of amino acid sequence differences between the two equine HAs located on the virus membrane-distal molecular surface. HAs of canine viruses are distinct in containing a Trp-222 → Leu substitution in the receptor binding site that influences specificity for receptor analogs. In the fusion subdomain of canine and recent equine virus HAs a unique difference is observed by comparison with all other HAs examined to date. Analyses of site-specific mutant HAs indicate that a single amino acid substitution, Thr-30 → Ser, influences interactions between N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the subdomain that are important in the structural changes required for membrane fusion activity. Both structural modifications may have facilitated the transmission of H3N8 influenza from horses to dogs.
- Divisions of Virology,Molecular Structure, and.
Organizational Affiliation: