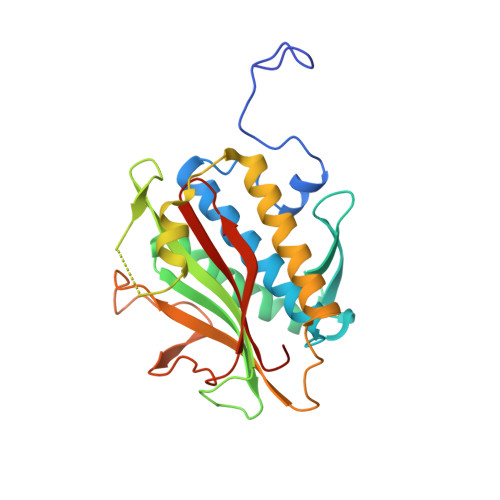
The Chromosome Axis Controls Meiotic Events through a Hierarchical Assembly of HORMA Domain Proteins.
Kim, Y., Rosenberg, S.C., Kugel, C.L., Kostow, N., Rog, O., Davydov, V., Su, T.Y., Dernburg, A.F., Corbett, K.D.(2014) Dev Cell 31: 487-502
- PubMed: 25446517
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.09.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4TRK, 4TZJ, 4TZL, 4TZM, 4TZN, 4TZO, 4TZQ, 4TZS - PubMed Abstract:
Proteins of the HORMA domain family play central, but poorly understood, roles in chromosome organization and dynamics during meiosis. In Caenorhabditis elegans, four such proteins (HIM-3, HTP-1, HTP-2, and HTP-3) have distinct but overlapping functions. Through combined biochemical, structural, and in vivo analysis, we find that these proteins form hierarchical complexes through binding of their HORMA domains to cognate peptides within their partners' C-terminal tails, analogous to the "safety belt" binding mechanism of Mad2. These interactions are critical for recruitment of HIM-3, HTP-1, and HTP-2 to chromosome axes. HTP-3, in addition to recruiting the other HORMA domain proteins to the axis, plays an independent role in sister chromatid cohesion and double-strand break formation. Finally, we find that mammalian HORMAD1 binds a motif found both at its own C terminus and at that of HORMAD2, indicating that this mode of intermolecular association is a conserved feature of meiotic chromosome structure in eukaryotes.
- Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA 94720-3220, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 4000 Jones Bridge Road, Chevy Chase, MD 20815, USA; Life Sciences Division, Department of Genome Dynamics, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA; California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: