The Mechanism of Dynein Light Chain LC8-mediated Oligomerization of the Ana2 Centriole Duplication Factor.
Slevin, L.K., Romes, E.M., Dandulakis, M.G., Slep, K.C.(2014) J Biological Chem 289: 20727-20739
- PubMed: 24920673
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.576041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QH7, 4QH8 - PubMed Abstract:
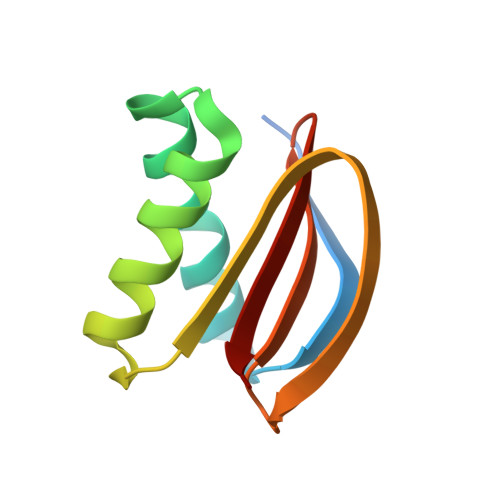
Centrioles play a key role in nucleating polarized microtubule networks. In actively dividing cells, centrioles establish the bipolar mitotic spindle and are essential for genomic stability. Drosophila anastral spindle-2 (Ana2) is a conserved centriole duplication factor. Although recent work has demonstrated that an Ana2-dynein light chain (LC8) centriolar complex is critical for proper spindle positioning in neuroblasts, how Ana2 and LC8 interact is yet to be established. Here we examine the Ana2-LC8 interaction and map two LC8-binding sites within the central region of Ana2, Ana2M (residues 156-251). Ana2 LC8-binding site 1 contains a signature TQT motif and robustly binds LC8 (KD of 1.1 μm), whereas site 2 contains a TQC motif and binds LC8 with lower affinity (KD of 13 μm). Both LC8-binding sites flank a predicted ~34-residue α-helix. We present two independent atomic structures of LC8 dimers in complex with Ana2 LC8-binding site 1 and site 2 peptides. The Ana2 peptides form β-strands that extend a central composite LC8 β-sandwich. LC8 recognizes the signature TQT motif in the first LC8 binding site of Ana2, forming extensive van der Waals contacts and hydrogen bonding with the peptide, whereas the Ana2 site 2 TQC motif forms a uniquely extended β-strand, not observed in other dynein light chain-target complexes. Size exclusion chromatography coupled with multiangle static light scattering demonstrates that LC8 dimers bind Ana2M sites and induce Ana2 tetramerization, yielding an Ana2M4-LC88 complex. LC8-mediated Ana2 oligomerization probably enhances Ana2 avidity for centriole-binding factors and may bridge multiple factors as required during spindle positioning and centriole biogenesis.
- From the Departments of Biology and.
Organizational Affiliation: