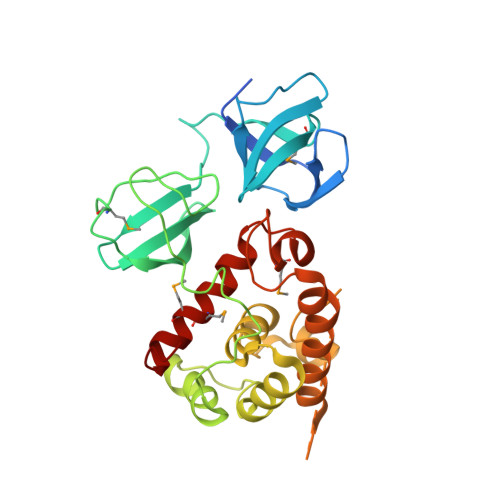
Structure of pneumococcal peptidoglycan hydrolase LytB reveals insights into the bacterial cell wall remodeling and pathogenesis.
Bai, X.H., Chen, H.J., Jiang, Y.L., Wen, Z., Huang, Y., Cheng, W., Li, Q., Qi, L., Zhang, J.R., Chen, Y., Zhou, C.Z.(2014) J Biological Chem 289: 23403-23416
- PubMed: 25002590
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.579714
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4Q2W - PubMed Abstract:
Streptococcus pneumoniae causes a series of devastating infections in humans. Previous studies have shown that the endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase LytB is critical for pneumococcal cell division and nasal colonization, but the biochemical mechanism of LytB action remains unknown. Here we report the 1.65 Å crystal structure of the catalytic domain (residues Lys-375-Asp-658) of LytB (termed LytBCAT), excluding the choline binding domain. LytBCAT consists of three structurally independent modules: SH3b, WW, and GH73. These modules form a "T-shaped" pocket that accommodates a putative tetrasaccharide-pentapeptide substrate of peptidoglycan. Structural comparison and simulation revealed that the GH73 module of LytB harbors the active site, including the catalytic residue Glu-564. In vitro assays of hydrolytic activity indicated that LytB prefers the peptidoglycan from the lytB-deficient pneumococci, suggesting the existence of a specific substrate of LytB in the immature peptidoglycan. Combined with in vitro cell-dispersing and in vivo cell separation assays, we demonstrated that all three modules are necessary for the optimal activity of LytB. Further functional analysis showed that the full catalytic activity of LytB is required for pneumococcal adhesion to and invasion into human lung epithelial cells. Structure-based alignment indicated that the unique modular organization of LytB is highly conserved in its orthologs from Streptococcus mitis group and Gemella species. These findings provided structural insights into the pneumococcal cell wall remodeling and novel hints for the rational design of therapeutic agents against pneumococcal growth and thereby the related diseases.
- From the Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230027, China and.
Organizational Affiliation: