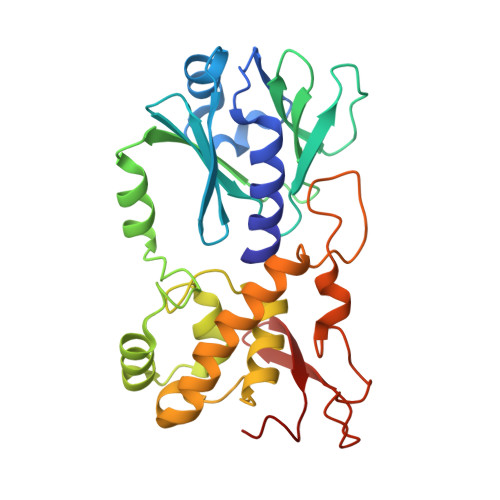
Zinc finger oxidation of Fpg/Nei DNA glycosylases by 2-thioxanthine: biochemical and X-ray structural characterization.
Biela, A., Coste, F., Culard, F., Guerin, M., Goffinont, S., Gasteiger, K., Ciesla, J., Winczura, A., Kazimierczuk, Z., Gasparutto, D., Carell, T., Tudek, B., Castaing, B.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 10748-10761
- PubMed: 25143530
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku613
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PCZ, 4PD2, 4PDG, 4PDI - PubMed Abstract:
DNA glycosylases from the Fpg/Nei structural superfamily are base excision repair enzymes involved in the removal of a wide variety of mutagen and potentially lethal oxidized purines and pyrimidines. Although involved in genome stability, the recent discovery of synthetic lethal relationships between DNA glycosylases and other pathways highlights the potential of DNA glycosylase inhibitors for future medicinal chemistry development in cancer therapy. By combining biochemical and structural approaches, the physical target of 2-thioxanthine (2TX), an uncompetitive inhibitor of Fpg, was identified. 2TX interacts with the zinc finger (ZnF) DNA binding domain of the enzyme. This explains why the zincless hNEIL1 enzyme is resistant to 2TX. Crystal structures of the enzyme bound to DNA in the presence of 2TX demonstrate that the inhibitor chemically reacts with cysteine thiolates of ZnF and induces the loss of zinc. The molecular mechanism by which 2TX inhibits Fpg may be generalized to all prokaryote and eukaryote ZnF-containing Fpg/Nei-DNA glycosylases. Cell experiments show that 2TX can operate in cellulo on the human Fpg/Nei DNA glycosylases. The atomic elucidation of the determinants for the interaction of 2TX to Fpg provides the foundation for the future design and synthesis of new inhibitors with high efficiency and selectivity.
- Centre de Biophysique Moléculaire, UPR4301, CNRS, rue Charles Sadron, 45100 Orléans cedex02, France Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics PAS, Pawinskiego 5A, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: