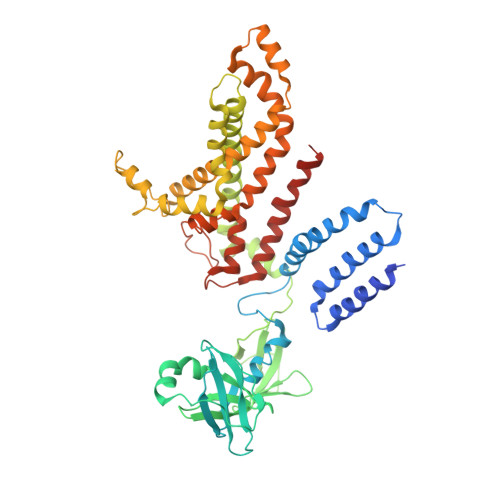
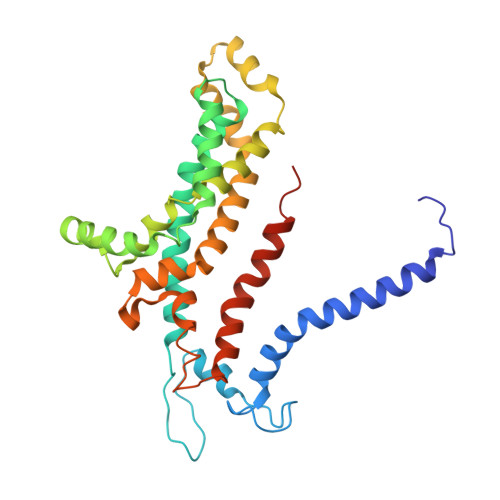
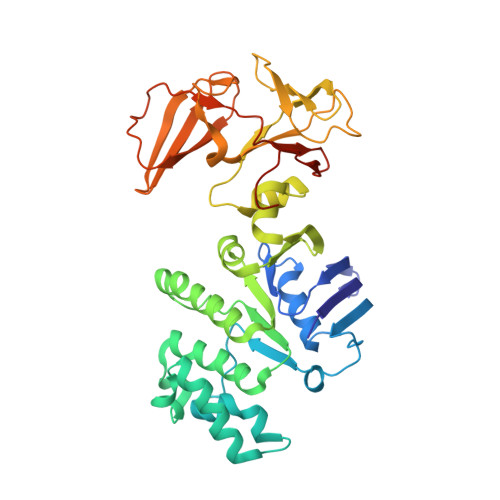
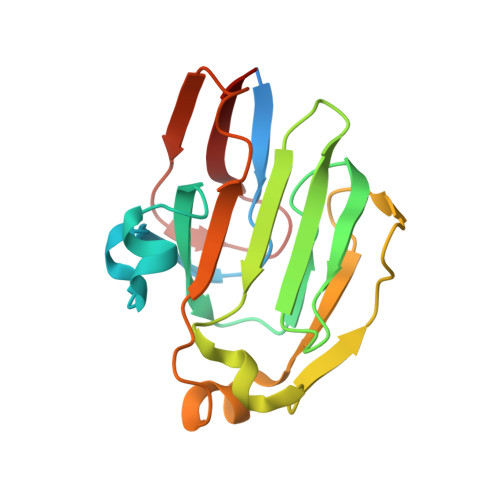
Carbon catabolite repression of the maltose transporter revealed by X-ray crystallography.
Chen, S., Oldham, M.L., Davidson, A.L., Chen, J.(2013) Nature 499: 364-368
- PubMed: 23770568
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12232
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JBW - PubMed Abstract:
Efficient carbon utilization is critical to the survival of microorganisms in competitive environments. To optimize energy usage, bacteria have developed an integrated control system to preferentially uptake carbohydrates that support rapid growth. The availability of a preferred carbon source, such as glucose, represses the synthesis and activities of proteins necessary for the transport and metabolism of secondary carbon sources. This regulatory phenomenon is defined as carbon catabolite repression. In enteric bacteria, the key player of carbon catabolite repression is a component of the glucose-specific phosphotransferase system, enzyme IIA (EIIA(Glc)). It is known that unphosphorylated EIIA(Glc) binds to and inhibits a variety of transporters when glucose is available. However, understanding the underlying molecular mechanism has been hindered by the complete absence of structures for any EIIA(Glc)-transporter complexes. Here we present the 3.9 Å crystal structure of Escherichia coli EIIA(Glc) in complex with the maltose transporter, an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. The structure shows that two EIIA(Glc) molecules bind to the cytoplasmic ATPase subunits, stabilizing the transporter in an inward-facing conformation and preventing the structural rearrangements necessary for ATP hydrolysis. We also show that the half-maximal inhibitory concentrations of the full-length EIIA(Glc) and an amino-terminal truncation mutant differ by 60-fold, consistent with the hypothesis that the amino-terminal region, disordered in the crystal structure, functions as a membrane anchor to increase the effective EIIA(Glc) concentration at the membrane. Together these data suggest a model of how the central regulatory protein EIIA(Glc) allosterically inhibits maltose uptake in E. coli.
- Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: