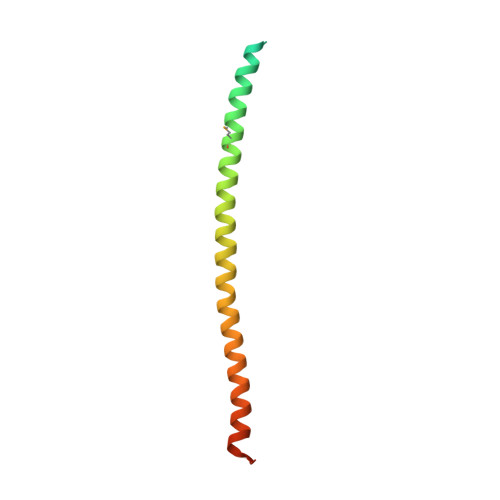
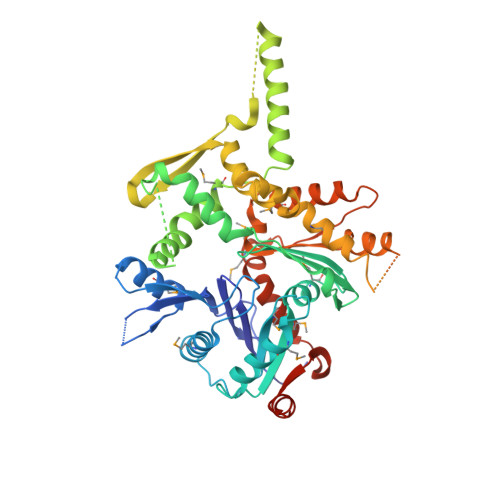
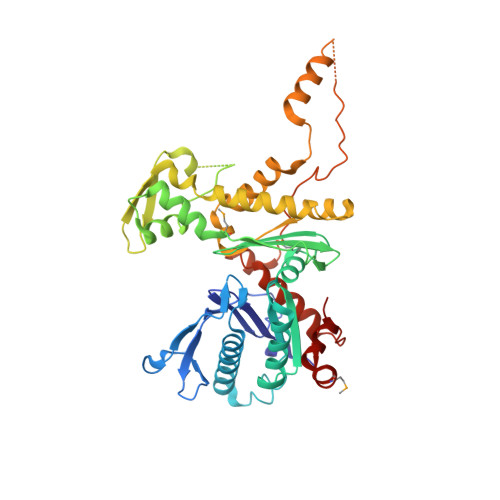
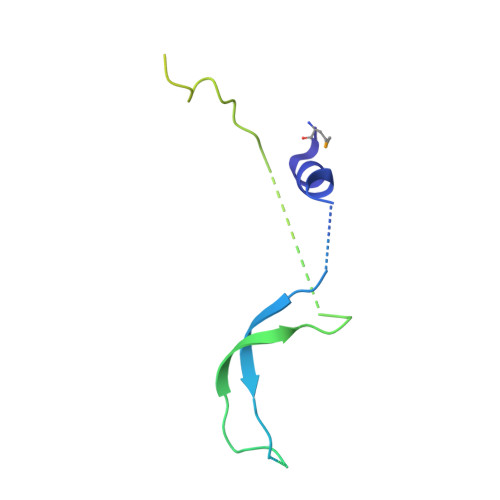
Structure of an actin-related subcomplex of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler.
Schubert, H.L., Wittmeyer, J., Kasten, M.M., Hinata, K., Rawling, D.C., Heroux, A., Cairns, B.R., Hill, C.P.(2013) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 3345-3350
- PubMed: 23401505
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215379110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I6M - PubMed Abstract:
The packaging of DNA into nucleosomal structures limits access for templated processes such as transcription and DNA repair. The repositioning or ejection of nucleosomes is therefore critically important for regulated events, including gene expression. This activity is provided by chromatin remodeling complexes, or remodelers, which are typically large, multisubunit complexes that use an ATPase subunit to translocate the DNA. Many remodelers contain pairs or multimers of actin-related proteins (ARPs) that contact the helicase-SANT-associated (HSA) domain within the catalytic ATPase subunit and are thought to regulate ATPase activity. Here, we determined the structure of a four-protein subcomplex within the SWI/SNF remodeler that comprises the Snf2 HSA domain, Arp7, Arp9, and repressor of Ty1 transposition, gene 102 (Rtt102). Surprisingly, unlike characterized actin-actin associations, the two ARPs pack like spoons and straddle the HSA domain, which forms a 92-Å-long helix. The ARP-HSA interactions are reminiscent of contacts between actin and many binding partners and are quite different from those in the Arp2/3 complex. Rtt102 wraps around one side of the complex in a highly extended conformation that contacts both ARPs and therefore stabilizes the complex, yet functions to reduce by ∼2.4-fold the remodeling and ATPase activity of complexes containing the Snf2 ATPase domain. Thus, our structure provides a foundation for developing models of remodeler function, including mechanisms of coupling between ARPs and the ATPase translocation activity.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: