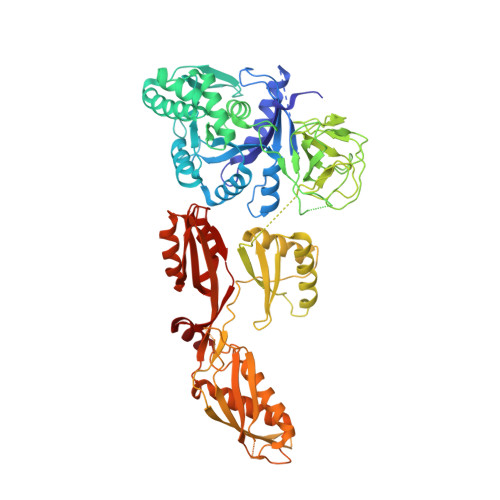
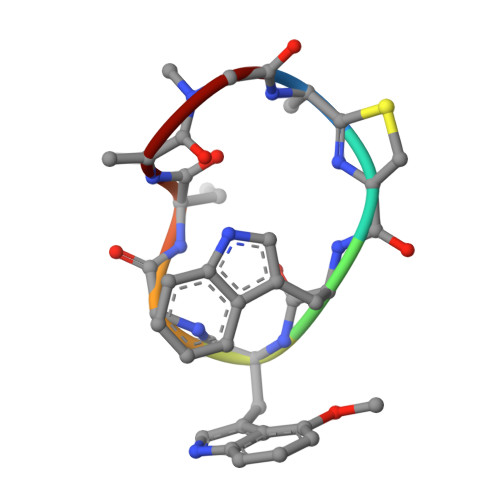
Identification of elongation factor g as the conserved cellular target of argyrin B.
Nyfeler, B., Hoepfner, D., Palestrant, D., Kirby, C.A., Whitehead, L., Yu, R., Deng, G., Caughlan, R.E., Woods, A.L., Jones, A.K., Barnes, S.W., Walker, J.R., Gaulis, S., Hauy, E., Brachmann, S.M., Krastel, P., Studer, C., Riedl, R., Estoppey, D., Aust, T., Movva, N.R., Wang, Z., Salcius, M., Michaud, G.A., McAllister, G., Murphy, L.O., Tallarico, J.A., Wilson, C.J., Dean, C.R.(2012) PLoS One 7: e42657-e42657
- PubMed: 22970117
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042657
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FN5 - PubMed Abstract:
Argyrins, produced by myxobacteria and actinomycetes, are cyclic octapeptides with antibacterial and antitumor activity. Here, we identify elongation factor G (EF-G) as the cellular target of argyrin B in bacteria, via resistant mutant selection and whole genome sequencing, biophysical binding studies and crystallography. Argyrin B binds a novel allosteric pocket in EF-G, distinct from the known EF-G inhibitor antibiotic fusidic acid, revealing a new mode of protein synthesis inhibition. In eukaryotic cells, argyrin B was found to target mitochondrial elongation factor G1 (EF-G1), the closest homologue of bacterial EF-G. By blocking mitochondrial translation, argyrin B depletes electron transport components and inhibits the growth of yeast and tumor cells. Further supporting direct inhibition of EF-G1, expression of an argyrin B-binding deficient EF-G1 L693Q variant partially rescued argyrin B-sensitivity in tumor cells. In summary, we show that argyrin B is an antibacterial and cytotoxic agent that inhibits the evolutionarily conserved target EF-G, blocking protein synthesis in bacteria and mitochondrial translation in yeast and mammalian cells.
- Developmental and Molecular Pathways, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, Cambridge, Massachussetts, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: