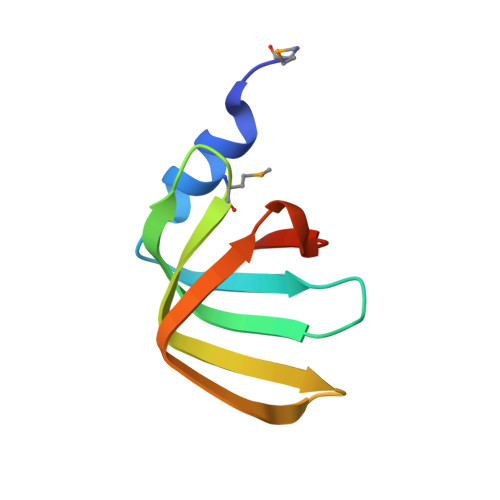
Crystal Structures of Lsm3, Lsm4 and Lsm5/6/7 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
Wu, D.H., Jiang, S.M., Bowler, M.W., Song, H.W.(2012) PLoS One 7: e36768-e36768
- PubMed: 22615807
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036768
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EMG, 4EMH, 4EMK - PubMed Abstract:
Sm-like (Lsm) proteins are ubiquitous and function in many aspects of RNA metabolism, including pre-mRNA splicing, nuclear RNA processing, mRNA decay and miRNA biogenesis. Here three crystal structures including Lsm3, Lsm4 and Lsm5/6/7 sub-complex from S. pombe are reported. These structures show that all the five individual Lsm subunits share a conserved Sm fold, and Lsm3, Lsm4, and Lsm5/6/7 form a heptamer, a trimer and a hexamer within the crystal lattice, respectively. Analytical ultracentrifugation indicates that Lsm3 and Lsm5/6/7 sub-complex exist in solution as a heptamer and a hexamer, respectively while Lsm4 undergoes a dynamic equilibrium between monomer and trimer in solution. RNA binding assays show that Lsm2/3 and Lsm5/6/7 bind to oligo(U) whereas no RNA binding is observed for Lsm3 and Lsm4. Analysis of the inter-subunit interactions in Lsm5/6/7 reveals the organization order among Lsm5, Lsm6 and Lsm7.
- Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, Singapore, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: