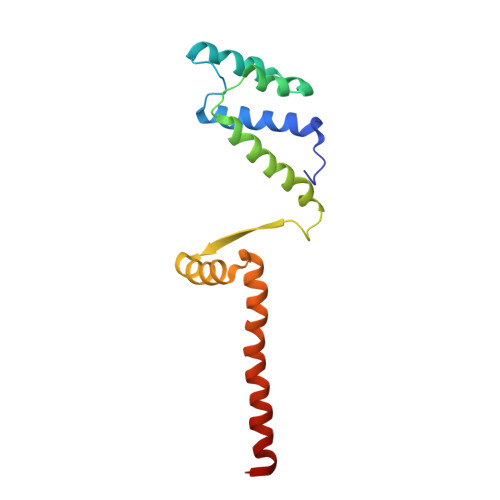
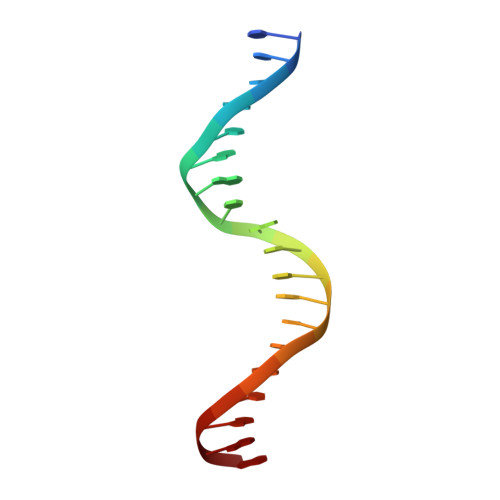
Molecular basis for a protein-mediated DNA-bridging mechanism that functions in condensation of the E. coli chromosome.
Dupaigne, P., Tonthat, N.K., Espeli, O., Whitfill, T., Boccard, F., Schumacher, M.A.(2012) Mol Cell 48: 560-571
- PubMed: 23084832
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VEA, 3VEB, 4D8J - PubMed Abstract:
The E. coli chromosome is condensed into insulated regions termed macrodomains (MDs), which are essential for genomic packaging. How chromosomal MDs are specifically organized and compacted is unknown. Here, we report studies revealing the molecular basis for Terminus-containing (Ter) chromosome condensation by the Ter-specific factor MatP. MatP contains a tripartite fold with a four-helix bundle DNA-binding motif, ribbon-helix-helix and C-terminal coiled-coil. Strikingly, MatP-matS structures show that the MatP coiled-coils form bridged tetramers that flexibly link distant matS sites. Atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy studies demonstrate that MatP alone loops DNA. Mutation of key coiled-coil residues destroys looping and causes a loss of Ter condensation in vivo. Thus, these data reveal the molecular basis for a protein-mediated DNA-bridging mechanism that mediates condensation of a large chromosomal domain in enterobacteria.
- Centre de Génétique Moléculaire du CNRS, Associé à l'Université Paris-Sud, 91198 Gif-sur-Yvette, France.
Organizational Affiliation: