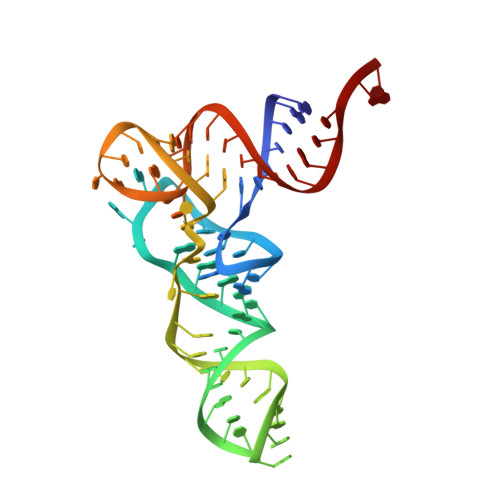
Translocation and rotation of tRNA during template-independent RNA polymerization by tRNA nucleotidyltransferase
Yamashita, S., Takeshita, D., Tomita, K.(2014) Structure 22: 315-325
- PubMed: 24389024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.12.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WFO, 3WFP, 3WFQ, 3WFR, 3WFS - PubMed Abstract:
The 3'-terminal CCA (CCA-3' at positions 74-76) of tRNA is synthesized by CCA-adding enzyme using CTP and ATP as substrates, without a nucleic acid template. In Aquifex aeolicus, CC-adding and A-adding enzymes collaboratively synthesize the CCA-3'. The mechanism of CCA-3' synthesis by these two enzymes remained obscure. We now present crystal structures representing CC addition onto tRNA by A. aeolicus CC-adding enzyme. After C₇₄ addition in an enclosed active pocket and pyrophosphate release, the tRNA translocates and rotates relative to the enzyme, and C₇₅ addition occurs in the same active pocket as C₇₄ addition. At both the C₇₄-adding and C₇₅-adding stages, CTP is selected by Watson-Crick-like hydrogen bonds between the cytosine of CTP and conserved Asp and Arg residues in the pocket. After C₇₄C₇₅ addition and pyrophosphate release, the tRNA translocates further and drops off the enzyme, and the CC-adding enzyme terminates RNA polymerization.
- Biomedical Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), 1-1-1, Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8566, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: