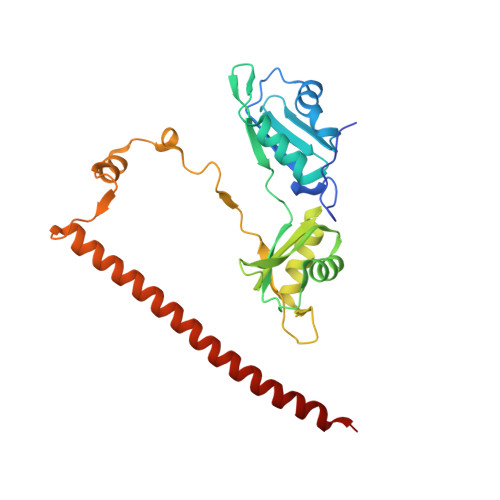
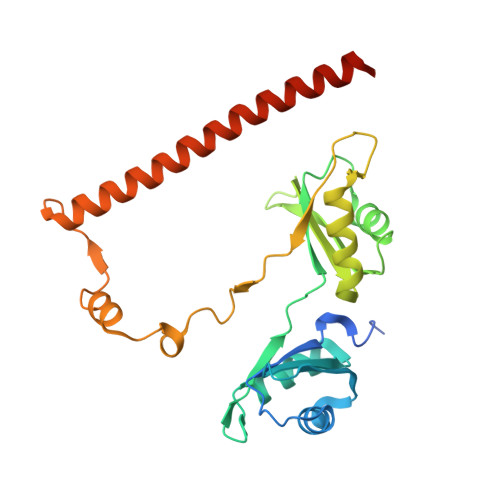
Structure of the heterodimer of human NONO and paraspeckle protein component 1 and analysis of its role in subnuclear body formation.
Passon, D.M., Lee, M., Rackham, O., Stanley, W.A., Sadowska, A., Filipovska, A., Fox, A.H., Bond, C.S.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 4846-4850
- PubMed: 22416126
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1120792109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SDE - PubMed Abstract:
Proteins of the Drosophila behavior/human splicing (DBHS) family include mammalian SFPQ (PSF), NONO (p54nrb), PSPC1, and invertebrate NONA and Hrp65. DBHS proteins are predominately nuclear, and are involved in transcriptional and posttranscriptional gene regulatory functions as well as DNA repair. DBHS proteins influence a wide gamut of biological processes, including the regulation of circadian rhythm, carcinogenesis, and progression of cancer. Additionally, mammalian DBHS proteins associate with the architectural long noncoding RNA NEAT1 (Menε/β) to form paraspeckles, subnuclear bodies that alter gene expression via the nuclear retention of RNA. Here we describe the crystal structure of the heterodimer of the multidomain conserved region of the DBHS proteins, PSPC1 and NONO. These proteins form an extensively intertwined dimer, consistent with the observation that the different DBHS proteins are typically copurified from mammalian cells, and suggesting that they act as obligate heterodimers. The PSPC1/NONO heterodimer has a right-handed antiparallel coiled-coil that positions two of four RNA recognition motif domains in an unprecedented arrangement on either side of a 20-Å channel. This configuration is supported by a protein:protein interaction involving the NONA/paraspeckle domain, which is characteristic of the DBHS family. By examining various mutants and truncations in cell culture, we find that DBHS proteins require an additional antiparallel coiled-coil emanating from either end of the dimer for paraspeckle subnuclear body formation. These results suggest that paraspeckles may potentially form through self-association of DBHS dimers into higher-order structures.
- School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Western Australia, Crawley, Western Australia 6009, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: