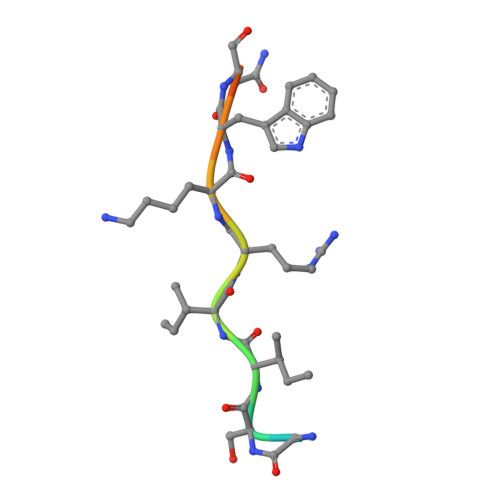
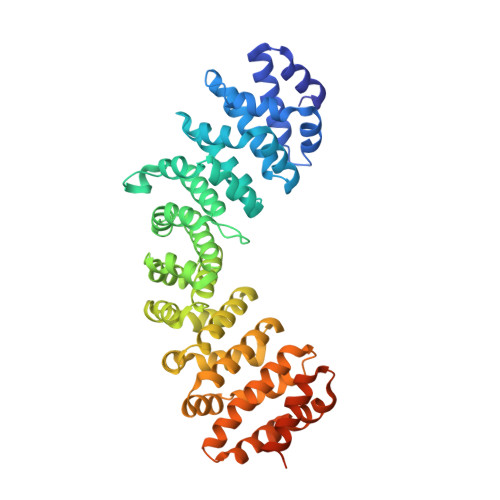A Minimal Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) in Human Phospholipid Scramblase 4 That Binds Only the Minor NLS-binding Site of Importin {alpha}1.
Lott, K., Bhardwaj, A., Sims, P.J., Cingolani, G.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 28160-28169
- PubMed: 21690087
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.228007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3Q5U - PubMed Abstract:
Importin α1 can bind classical nuclear localization signals (NLSs) in two NLS-binding sites, known as "major" and "minor." The major site is located between ARM repeats 2-4, whereas the minor site spans ARM 7-8. In this study, we have characterized the cellular localization of human phospholipid scramblase 4 (hPLSCR4), a member of the phospholipid scramblase protein family. We identified a minimal NLS in hPLSCR4 ((273)GSIIRKWN(280)) that contains only two basic amino acids. This NLS is both necessary for nuclear localization of hPLSCR4 in transfected HeLa cells and sufficient for nuclear import of a non-diffusible cargo in permeabilized cells. Mutation of only one of the two basic residues, Arg(277), correlates with loss of nuclear localization, suggesting this amino acid plays a key role in nuclear transport. Crystallographic analysis of mammalian importin α1 in complex with the hPLSCR4-NLS reveals this minimal NLS binds specifically and exclusively to the minor binding site of importin α. These data provide the first structural and functional evidence of a novel NLS-binding mode in importin α1 that uses only the minor groove as the exclusive site for nuclear import of nonclassical cargos.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19107, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: