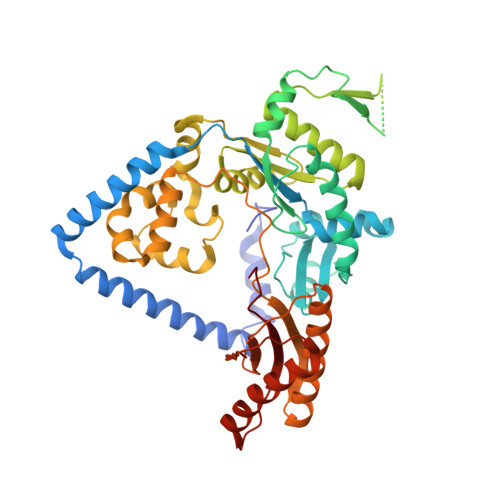
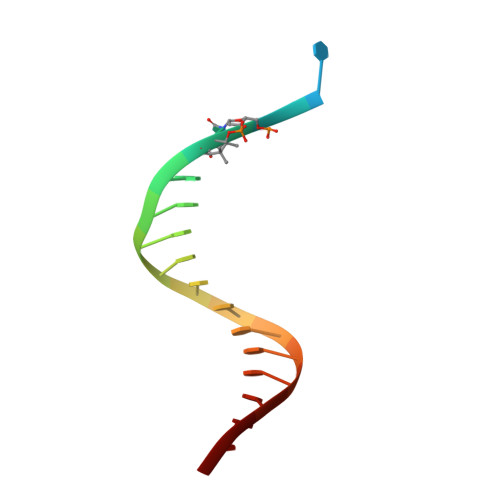
Role of human DNA polymerase kappa in extension opposite from a cis-syn thymine dimer.
Vasquez-Del Carpio, R., Silverstein, T.D., Lone, S., Johnson, R.E., Prakash, L., Prakash, S., Aggarwal, A.K.(2011) J Mol Biology 408: 252-261
- PubMed: 21354175
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.02.042
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3PZP - PubMed Abstract:
Exposure of DNA to UV radiation causes covalent linkages between adjacent pyrimidines. The most common lesion found in DNA from these UV-induced linkages is the cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer. Human DNA polymerase κ (Polκ), a member of the Y-family of DNA polymerases, is unable to insert nucleotides opposite the 3'T of a cis-syn T-T dimer, but it can efficiently extend from a nucleotide inserted opposite the 3'T of the dimer by another DNA polymerase. We present here the structure of human Polκ in the act of inserting a nucleotide opposite the 5'T of the cis-syn T-T dimer. The structure reveals a constrained active-site cleft that is unable to accommodate the 3'T of a cis-syn T-T dimer but is remarkably well adapted to accommodate the 5'T via Watson-Crick base pairing, in accord with a proposed role for Polκ in the extension reaction opposite from cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in vivo.
- Department of Structural and Chemical Biology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, Box 1677, 1425 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10029, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: