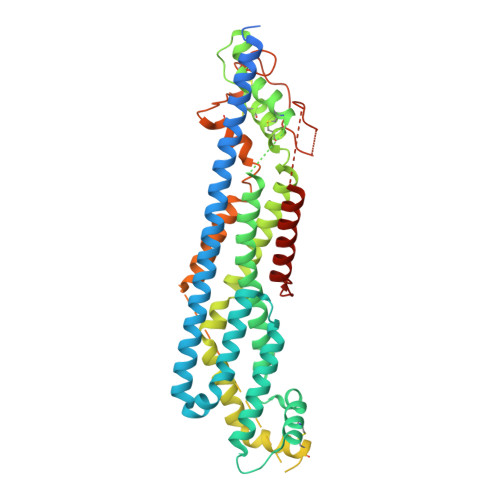
Structure of the protein core of the glypican Dally-like and localization of a region important for hedgehog signaling.
Kim, M.S., Saunders, A.M., Hamaoka, B.Y., Beachy, P.A., Leahy, D.J.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 13112-13117
- PubMed: 21828006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1109877108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ODN - PubMed Abstract:
Glypicans are heparan sulfate proteoglycans that modulate the signaling of multiple growth factors active during animal development, and loss of glypican function is associated with widespread developmental abnormalities. Glypicans consist of a conserved, approximately 45-kDa N-terminal protein core region followed by a stalk region that is tethered to the cell membrane by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor. The stalk regions are predicted to be random coil but contain a variable number of attachment sites for heparan sulfate chains. Both the N-terminal protein core and the heparan sulfate attachments are important for glypican function. We report here the 2.4-Å crystal structure of the N-terminal protein core region of the Drosophila glypican Dally-like (Dlp). This structure reveals an elongated, α-helical fold for glypican core regions that does not appear homologous to any known structure. The Dlp core protein is required for normal responsiveness to Hedgehog (Hh) signals, and we identify a localized region on the Dlp surface important for mediating its function in Hh signaling. Purified Dlp protein core does not, however, interact appreciably with either Hh or an Hh:Ihog complex.
- Department of Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: