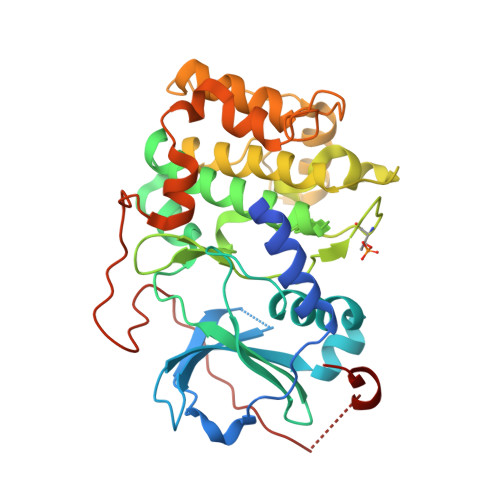
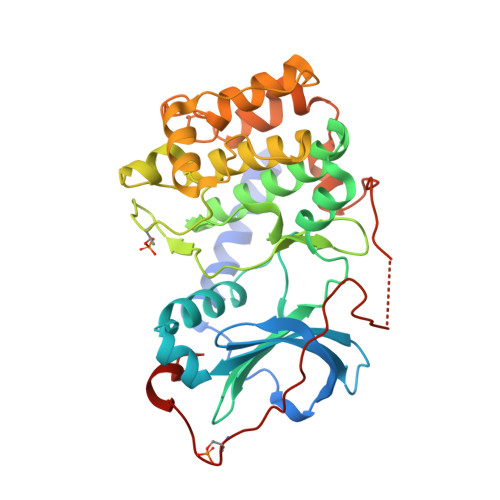
Dynamics connect substrate recognition to catalysis in protein kinase A.
Masterson, L.R., Cheng, C., Yu, T., Tonelli, M., Kornev, A., Taylor, S.S., Veglia, G.(2010) Nat Chem Biol 6: 821-828
- PubMed: 20890288
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.452
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3O7L - PubMed Abstract:
Atomic resolution studies of protein kinases have traditionally been carried out in the inhibitory state, limiting our current knowledge on the mechanisms of substrate recognition and catalysis. Using NMR, X-ray crystallography and thermodynamic measurements, we analyzed the substrate recognition process of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), finding that entropy and protein dynamics play a prominent role. The nucleotide acts as a dynamic and allosteric activator by coupling the two lobes of apo PKA, enhancing the enzyme dynamics synchronously and priming it for catalysis. The formation of the ternary complex is entropically driven, and NMR spin relaxation data reveal that both substrate and PKA are dynamic in the closed state. Our results show that the enzyme toggles between open and closed states, which indicates that a conformational selection rather than an induced-fit mechanism governs substrate recognition.
- Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: