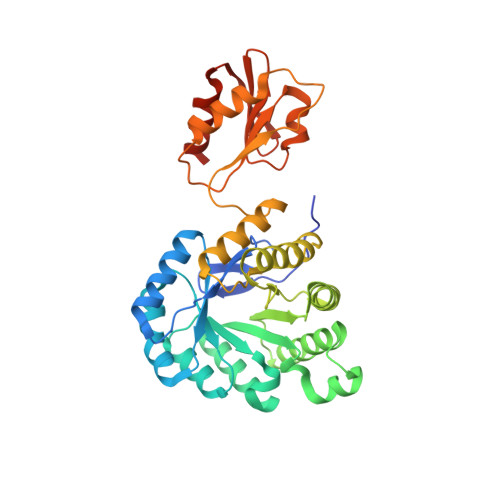
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: crystal structure of the [4Fe-4S] cluster protein IspG.
Lee, M., Grawert, T., Quitterer, F., Rohdich, F., Eppinger, J., Eisenreich, W., Bacher, A., Groll, M.(2010) J Mol Biology 404: 600-610
- PubMed: 20932974
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.050
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NOY - PubMed Abstract:
IspG protein serves as the penultimate enzyme of the recently discovered non-mevalonate pathway for the biosynthesis of the universal isoprenoid precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. The enzyme catalyzes the reductive ring opening of 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, which affords 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate. The protein was crystallized under anaerobic conditions, and its three-dimensional structure was determined to a resolution of 2.7 Å. Each subunit of the c(2) symmetric homodimer folds into two domains connected by a short linker sequence. The N-terminal domain (N domain) is an eight-stranded β barrel that belongs to the large TIM-barrel superfamily. The C-terminal domain (C domain) consists of a β sheet that is flanked on both sides by helices. One glutamate and three cysteine residues of the C domain coordinate a [4Fe-4S] cluster. Homodimer formation involves an extended contact area (about 1100 Å(2)) between helices 8 and 9 of each respective β barrel. Moreover, each C domain contacts the N domain of the partner subunit, but the interface regions are small (about 430 Å(2)). We propose that the enzyme substrate binds to the positively charged surface area at the C-terminal pole of the β barrel. The C domain carrying the iron-sulfur cluster could then move over to form a closed conformation where the substrate is sandwiched between the N domain and the C domain. This article completes the set of three-dimensional structures of the non-mevalonate pathway enzymes, which are of specific interest as potential targets for tuberculostatic and antimalarial drugs.
- Lehrstuhl für Biochemie, Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich, Department Chemie, Technische Universität München, Lichtenbergstrasse 4, D-85747 Garching, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: