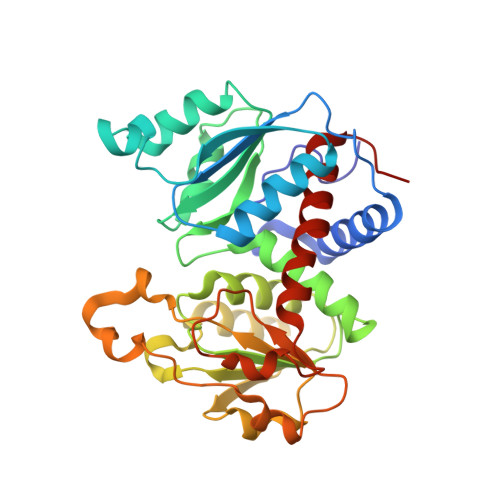
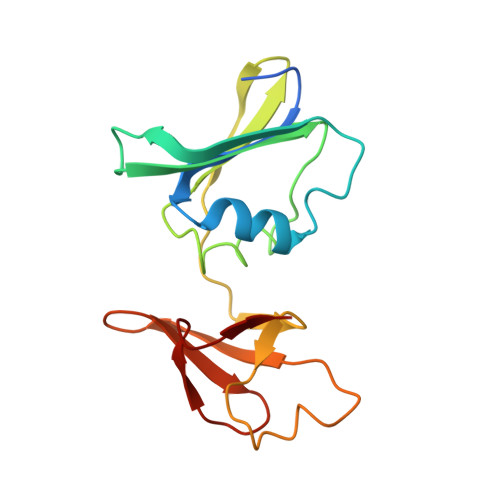
The Pathway of Product Release from the R State of Aspartate Transcarbamoylase.
Mendes, K.R., Kantrowitz, E.R.(2010) J Mol Biology 401: 940-948
- PubMed: 20620149
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.07.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3MPU - PubMed Abstract:
The pathway of product release from the R state of aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase; EC 2.1.3.2, aspartate carbamoyltransferase) has been determined here by solving the crystal structure of Escherichia coli ATCase locked in the R quaternary structure by specific introduction of disulfide bonds. ATCase displays ordered substrate binding and product release, remaining in the R state until substrates are exhausted. The structure reported here represents ATCase in the R state bound to the final product molecule, phosphate. This structure has been difficult to obtain previously because the enzyme relaxes back to the T state after the substrates are exhausted. Hence, cocrystallizing the wild-type enzyme with phosphate results in a T-state structure. In this structure of the enzyme trapped in the R state with specific disulfide bonds, we observe two phosphate molecules per active site. The position of the first phosphate corresponds to the position of the phosphate of carbamoyl phosphate (CP) and the position of the phosphonate of N-phosphonacetyl-l-aspartate. However, the second, more weakly bound phosphate is bound in a positively charged pocket that is more accessible to the surface than the other phosphate. The second phosphate appears to be on the path that phosphate would have to take to exit the active site. Our results suggest that phosphate dissociation and CP binding can occur simultaneously and that the dissociation of phosphate may actually promote the binding of CP for more efficient catalysis.
- Department of Chemistry, Boston College, Merkert Chemistry Center, Chestnut Hill, MA 02467-3807, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: