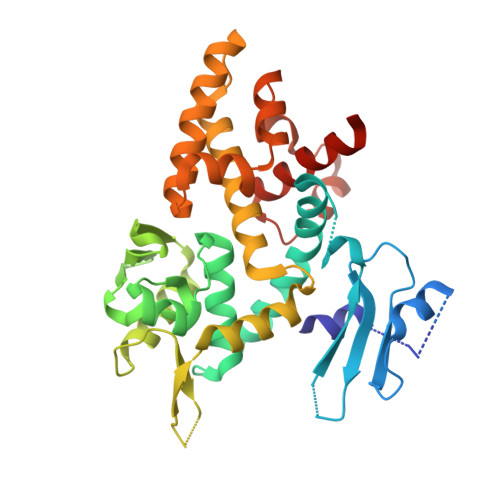
Crystal structure of a bacterial topoisomerase IB in complex with DNA reveals a secondary DNA binding site.
Patel, A., Yakovleva, L., Shuman, S., Mondragon, A.(2010) Structure 18: 725-733
- PubMed: 20541510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.03.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3M4A - PubMed Abstract:
Type IB DNA topoisomerases (TopIB) are monomeric enzymes that relax supercoils by cleaving and resealing one strand of duplex DNA within a protein clamp that embraces a approximately 21 DNA segment. A longstanding conundrum concerns the capacity of TopIB enzymes to stabilize intramolecular duplex DNA crossovers and form protein-DNA synaptic filaments. Here we report a structure of Deinococcus radiodurans TopIB in complex with a 12 bp duplex DNA that demonstrates a secondary DNA binding site located on the surface of the C-terminal domain. It comprises a distinctive interface with one strand of the DNA duplex and is conserved in all TopIB enzymes. Modeling of a TopIB with both DNA sites suggests that the secondary site could account for DNA crossover binding, nucleation of DNA synapsis, and generation of a filamentous plectoneme. Mutations of the secondary site eliminate synaptic plectoneme formation without affecting DNA cleavage or supercoil relaxation.
- Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology, Northwestern University, 2205 Tech Drive, Evanston, IL 60208, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: