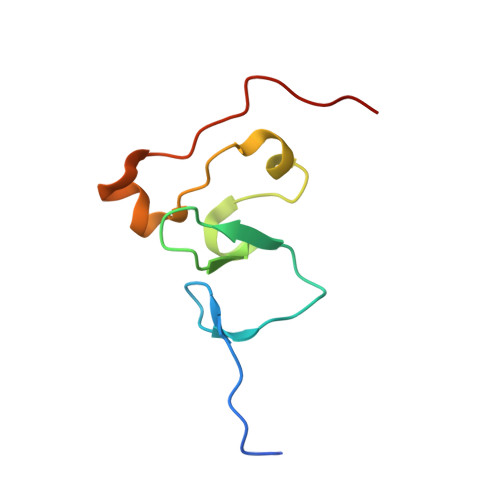
Recognition of histone H3K4 trimethylation by the plant homeodomain of PHF2 modulates histone demethylation.
Wen, H., Li, J., Song, T., Lu, M., Kan, P.Y., Lee, M.G., Sha, B., Shi, X.(2010) J Biological Chem 285: 9322-9326
- PubMed: 20129925
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C109.097667
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KQI - PubMed Abstract:
Distinct lysine methylation marks on histones create dynamic signatures deciphered by the "effector" modules, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We identified the plant homeodomain- and Jumonji C domain-containing protein PHF2 as a novel histone H3K9 demethylase. We show in biochemical and crystallographic analyses that PHF2 recognizes histone H3K4 trimethylation through its plant homeodomain finger and that this interaction is essential for PHF2 occupancy and H3K9 demethylation at rDNA promoters. Our study provides molecular insights into the mechanism by which distinct effector domains within a protein cooperatively modulate the "cross-talk" of histone modifications.
- Departments of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Houston, Texas 77030; Centers for Cancer Epigenetics, Houston, Texas 77030; Stem Cell and Developmental Biology, Houston, Texas 77030.
Organizational Affiliation: