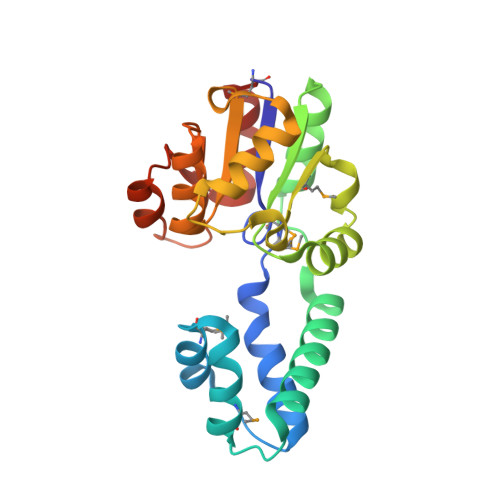
Structure of a putative beta-phosphoglucomutase (TM1254) from Thermotoga maritima.
Strange, R.W., Antonyuk, S.V., Ellis, M.J., Bessho, Y., Kuramitsu, S., Shinkai, A., Yokoyama, S., Hasnain, S.S.(2009) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 65: 1218-1221
- PubMed: 20054115
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309109046302
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KBB - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of TM1254, a putative beta-phosphoglucomutase from T. maritima, was determined to 1.74 A resolution in a high-throughput structural genomics programme. Diffraction data were obtained from crystals belonging to space group P22(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 48.16, b = 66.70, c = 83.80 A, and were refined to an R factor of 19.2%. The asymmetric unit contained one protein molecule which is comprised of two domains. Structural homologues were found from protein databases that confirmed a strong resemblance between TM1254 and members of the haloacid dehalogenase (HAD) hydrolase family.
- Molecular Biophysics Group, School of Biological Sciences, University of Liverpool, Crown Street, Liverpool L69 7ZB, England. r.strange@liverpool.ac.uk
Organizational Affiliation: