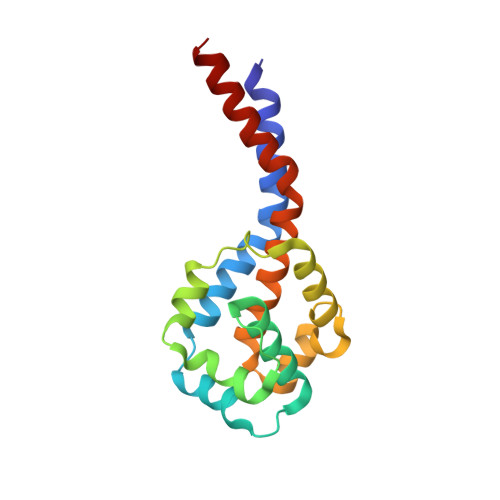
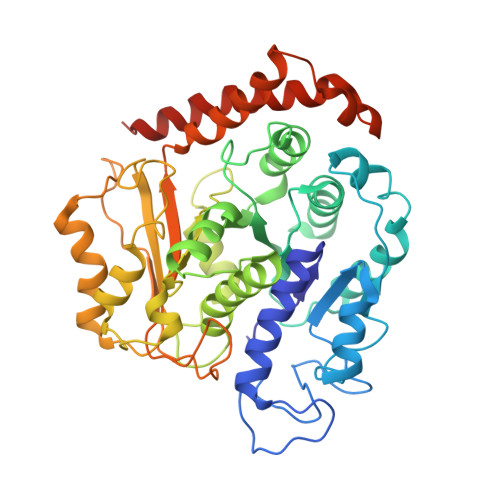
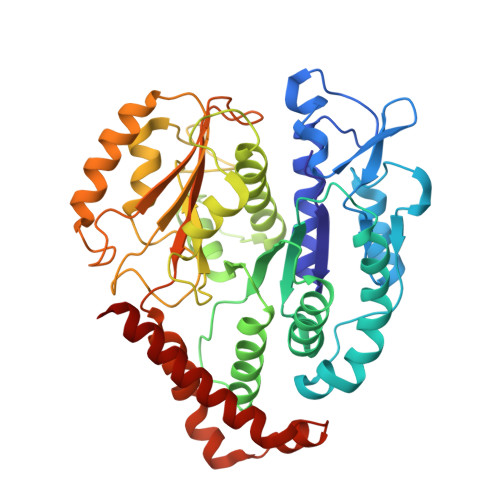
Structural basis for microtubule binding and release by dynein.
Redwine, W.B., Hernandez-Lopez, R., Zou, S., Huang, J., Reck-Peterson, S.L., Leschziner, A.E.(2012) Science 337: 1532-1536
- PubMed: 22997337
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224151
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3J1T, 3J1U - PubMed Abstract:
Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule-based motor required for intracellular transport and cell division. Its movement involves coupling cycles of track binding and release with cycles of force-generating nucleotide hydrolysis. How this is accomplished given the ~25 nanometers separating dynein's track- and nucleotide-binding sites is not understood. Here, we present a subnanometer-resolution structure of dynein's microtubule-binding domain bound to microtubules by cryo-electron microscopy that was used to generate a pseudo-atomic model of the complex with molecular dynamics. We identified large rearrangements triggered by track binding and specific interactions, confirmed by mutagenesis and single-molecule motility assays, which tune dynein's affinity for microtubules. Our results provide a molecular model for how dynein's binding to microtubules is communicated to the rest of the motor.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Harvard University, 52 Oxford Street, Cambridge, MA 02138, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: