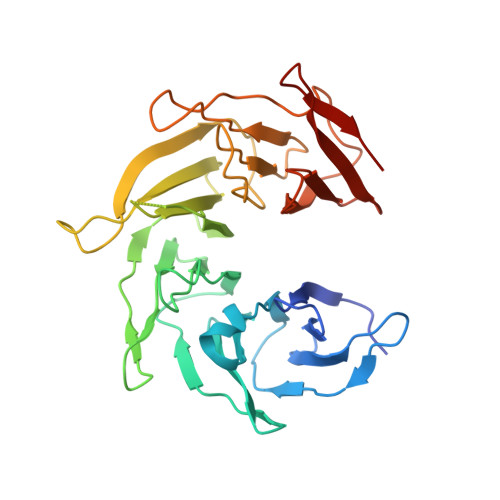
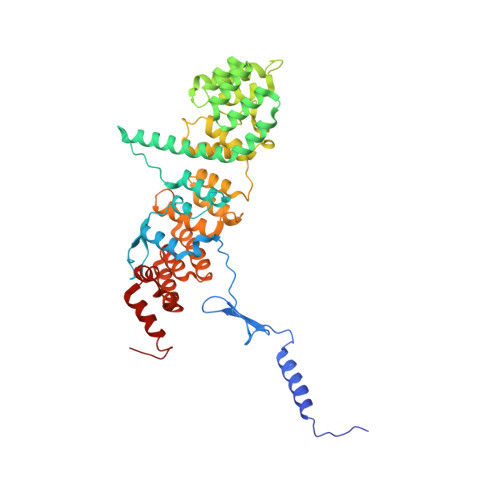
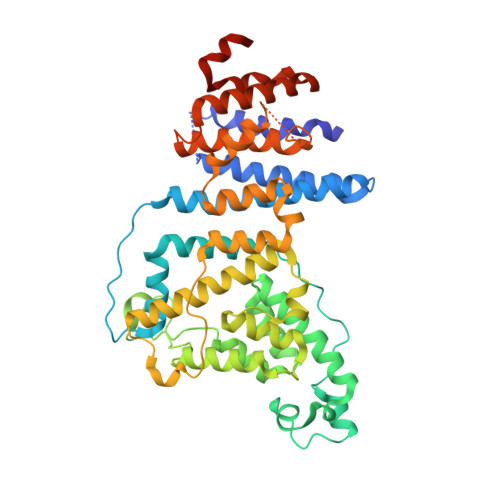
Structure of a trimeric nucleoporin complex reveals alternate oligomerization states.
Nagy, V., Hsia, K.C., Debler, E.W., Kampmann, M., Davenport, A.M., Blobel, G., Hoelz, A.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 17693-17698
- PubMed: 19805193
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909373106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3IKO - PubMed Abstract:
The heptameric Nup84 complex constitutes an evolutionarily conserved building block of the nuclear pore complex. Here, we present the crystal structure of the heterotrimeric Sec13 x Nup145C x Nup84 complex, the centerpiece of the heptamer, at 3.2-A resolution. Nup84 forms a U-shaped alpha-helical solenoid domain, topologically similar to two other members of the heptamer, Nup145C and Nup85. The interaction between Nup84 and Nup145C is mediated via a hydrophobic interface located in the kink regions of the two solenoids that is reinforced by additional interactions of two long Nup84 loops. The Nup84 binding site partially overlaps with the homo-dimerization interface of Nup145C, suggesting competing binding events. Fitting of the elongated Z-shaped heterotrimer into electron microscopy (EM) envelopes of the heptamer indicates that structural changes occur at the Nup145C x Nup84 interface. Docking the crystal structures of all heptamer components into the EM envelope constitutes a major advance toward the completion of the structural characterization of the Nup84 complex.
- Laboratory of Cell Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: