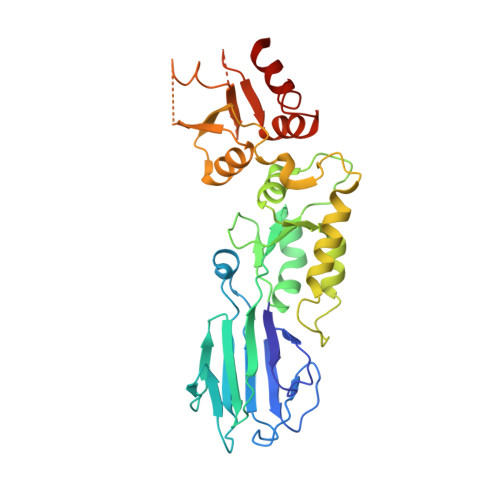
Nbs1 flexibly tethers Ctp1 and Mre11-Rad50 to coordinate DNA double-strand break processing and repair.
Williams, R.S., Dodson, G.E., Limbo, O., Yamada, Y., Williams, J.S., Guenther, G., Classen, S., Glover, J.N., Iwasaki, H., Russell, P., Tainer, J.A.(2009) Cell 139: 87-99
- PubMed: 19804755
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.033
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HUE, 3HUF - PubMed Abstract:
The Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (Nbs1) subunit of the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex protects genome integrity by coordinating double-strand break (DSB) repair and checkpoint signaling through undefined interactions with ATM, MDC1, and Sae2/Ctp1/CtIP. Here, fission yeast and human Nbs1 structures defined by X-ray crystallography and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) reveal Nbs1 cardinal features: fused, extended, FHA-BRCT(1)-BRCT(2) domains flexibly linked to C-terminal Mre11- and ATM-binding motifs. Genetic, biochemical, and structural analyses of an Nbs1-Ctp1 complex show Nbs1 recruits phosphorylated Ctp1 to DSBs via binding of the Nbs1 FHA domain to a Ctp1 pThr-Asp motif. Nbs1 structures further identify an extensive FHA-BRCT interface, a bipartite MDC1-binding scaffold, an extended conformational switch, and the molecular consequences associated with cancer predisposing Nijmegen breakage syndrome mutations. Tethering of Ctp1 to a flexible Nbs1 arm suggests a mechanism for restricting DNA end processing and homologous recombination activities of Sae2/Ctp1/CtIP to the immediate vicinity of DSBs.
- Department of Molecular Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: