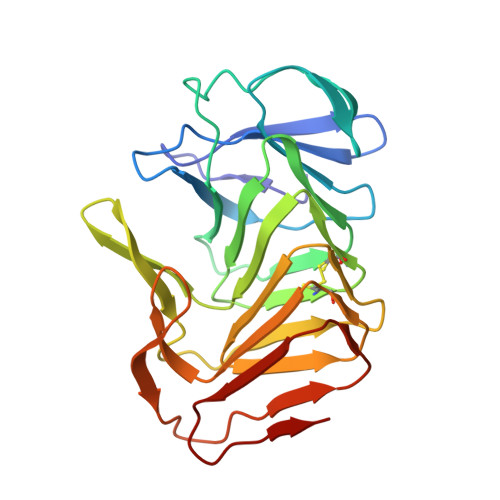
Structural and functional studies of truncated hemolysin A from Proteus mirabilis.
Weaver, T.M., Hocking, J.M., Bailey, L.J., Wawrzyn, G.T., Howard, D.R., Sikkink, L.A., Ramirez-Alvarado, M., Thompson, J.R.(2009) J Biological Chem 284: 22297-22309
- PubMed: 19494116
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.014431
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FY3 - PubMed Abstract:
In this study we analyzed the structure and function of a truncated form of hemolysin A (HpmA265) from Proteus mirabilis using a series of functional and structural studies. Hemolysin A belongs to the two-partner secretion pathway. The two-partner secretion pathway has been identified as the most common protein secretion pathway among Gram-negative bacteria. Currently, the mechanism of action for the two-partner hemolysin members is not fully understood. In this study, hemolysis experiments revealed a unidirectional, cooperative, biphasic activity profile after full-length, inactive hemolysin A was seeded with truncated hemolysin A. We also solved the first x-ray structure of a TpsA hemolysin. The truncated hemolysin A formed a right-handed parallel beta-helix with three adjoining segments of anti-parallel beta-sheet. A CXXC disulfide bond, four buried solvent molecules, and a carboxyamide ladder were all located at the third complete beta-helix coil. Replacement of the CXXC motif led to decreased activity and stability according to hemolysis and CD studies. Furthermore, the crystal structure revealed a sterically compatible, dry dimeric interface formed via anti-parallel beta-sheet interactions between neighboring beta-helix monomers. Laser scanning confocal microscopy further supported the unidirectional interconversion of full-length hemolysin A. From these results, a model has been proposed, where cooperative, beta-strand interactions between HpmA265 and neighboring full-length hemolysin A molecules, facilitated in part by the highly conserved CXXC pattern, account for the template-assisted hemolysis.
- Departments of Chemistry, La Crosse, Wisconsin 54601.
Organizational Affiliation: