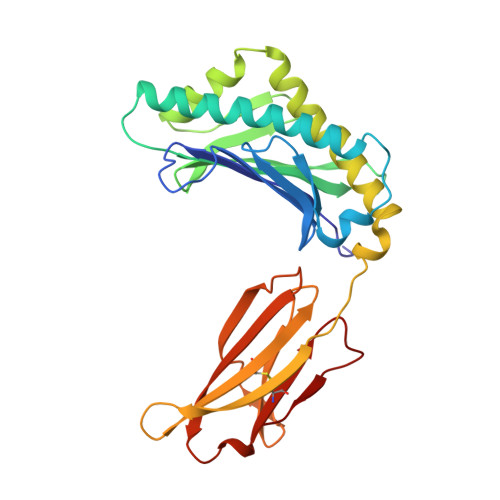
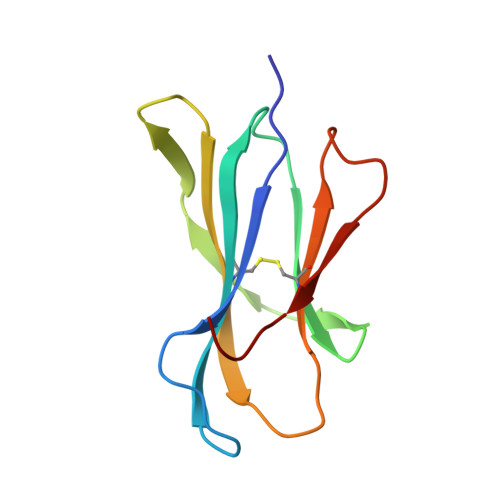
Structural basis of pH-dependent antibody binding by the neonatal Fc receptor.
Vaughn, D.E., Bjorkman, P.J.(1998) Structure 6: 63-73
- PubMed: 9493268
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00008-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FRU - PubMed Abstract:
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) mediates the transcytosis of maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) across fetal and/or neonatal tissues for the acquisition of passive immunity. In adults, FcRn is involved in the maintenance of high serum IgG levels. Both processes are mediated by pH-dependent IgG binding to FcRn-FcRn binds to IgG with nanomolar affinity at pH 6, but shows no detectable binding at pH 7.5. At pH 6, FcRn is more thermally stable and the dissociation rate of its light chain is an order of magnitude slower than at pH 8.0. Comparison of the structures of FcRn at pH 6.5 and pH 8 allows an analysis of the structural basis for the receptor's pH-dependent ligand binding and stability. We have determined the structure of FcRn at pH 8 and compared it to a further refined version of the structure at pH 6.5. An extensive ordered carbohydrate structure is observed at both pH values. The two structures are very similar; thus the pH dependence of FcRn stability and affinity for IgG can be attributed to chemical properties of the structures themselves, rather than mechanisms that rely on conformational changes. The pH-dependent properties are mediated by electrostatic interactions involving histidine residues, which are more favorable for the protonated form of histidine that predominates at acidic pH values. No major conformational change is observed between the pH 6.5 and pH 8 structures of FcRn that could account for the differences in affinity for IgG. The pH dependence of IgG binding to FcRn can therefore primarily be attributed to titration of histidine residues on Fc that interact with anionic pockets on the receptor. The FcRn dimer, which is required for high affinity binding of IgG, is itself stabilized at acidic pH by histidine-mediated salt bridges and a sidechain rearrangement that creates a more favorable interaction with an anionic pocket at pH 6.5 relative to pH 8. FcRn dimerization is facilitated by reciprocal interactions in which carbohydrate from one receptor molecule binds to protein residues from the dimer-related receptor molecule to form a 'carbohydrate handshake'.
- Division of Biology, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena 91125, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: