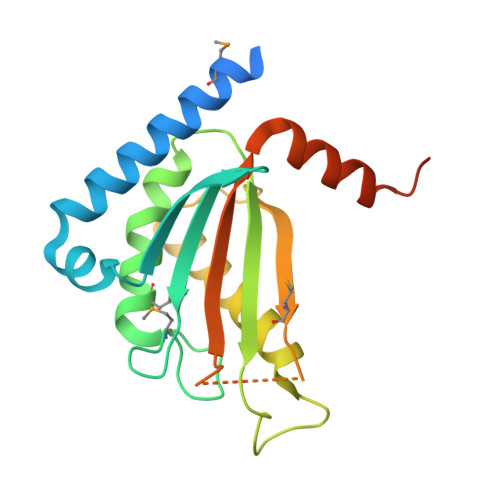
Stator assembly and activation mechanism of the flagellar motor by the periplasmic region of MotB
Kojima, S., Imada, K., Sakuma, M., Sudo, Y., Kojima, C., Minamino, T., Homma, M., Namba, K.(2009) Mol Microbiol 73: 710-718
- PubMed: 19627504
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06802.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZOV, 2ZVY, 2ZVZ - PubMed Abstract:
Torque generation in the Salmonella flagellar motor is coupled to translocation of H(+) ions through the proton-conducting channel of the Mot protein stator complex. The Mot complex is believed to be anchored to the peptidoglycan (PG) layer by the putative peptidoglycan-binding (PGB) domain of MotB. Proton translocation is activated only when the stator is installed into the motor. We report the crystal structure of a C-terminal periplasmic fragment of MotB (MotB(C)) that contains the PGB domain and includes the entire periplasmic region essential for motility. Structural and functional analyses indicate that the PGB domains must dimerize in order to form the proton-conducting channel. Drastic conformational changes in the N-terminal portion of MotB(C) are required both for PG binding and the proton channel activation.
- Division of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Chikusa-Ku, Nagoya 464-8602, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: