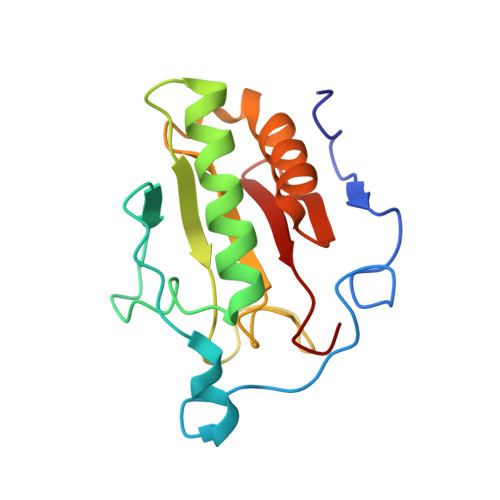
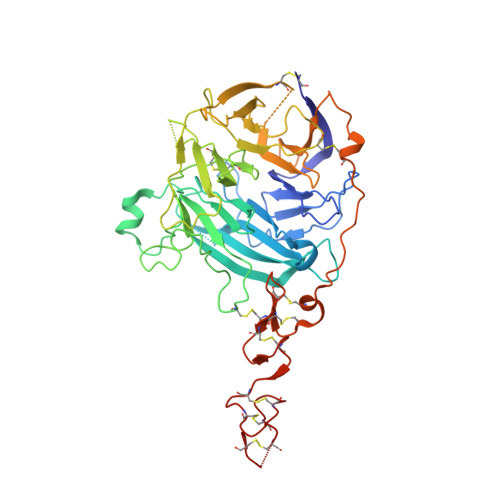
Structural Insights Into Hedgehog Ligand Sequestration by the Human Hedgehog-Interacting Protein Hip
Bishop, B., Aricescu, A.R., Harlos, K., O'Callaghan, C.A., Jones, E.Y., Siebold, C.(2009) Nat Struct Mol Biol 16: 698
- PubMed: 19561611
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1607
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WFQ, 2WFR, 2WFT, 2WFX, 2WG3, 2WG4 - PubMed Abstract:
Hedgehog (Hh) morphogens have fundamental roles in development, whereas dysregulation of Hh signaling leads to disease. Multiple cell-surface receptors are responsible for transducing and/or regulating Hh signals. Among these, the Hedgehog-interacting protein (Hhip) is a highly conserved, vertebrate-specific inhibitor of Hh signaling. We have solved a series of crystal structures for the human HHIP ectodomain and Desert hedgehog (DHH) in isolation, as well as HHIP in complex with DHH (HHIP-DHH) and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) (HHIP-Shh), with and without Ca2+. The interaction determinants, confirmed by biophysical studies and mutagenesis, reveal previously uncharacterized and distinct functions for the Hh Zn2+ and Ca2+ binding sites--functions that may be common to all vertebrate Hh proteins. Zn2+ makes a key contribution to the Hh-HHIP interface, whereas Ca2+ is likely to prevent electrostatic repulsion between the two proteins, suggesting an important modulatory role. This interplay of several metal binding sites suggests a tuneable mechanism for regulation of Hh signaling.
- Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: