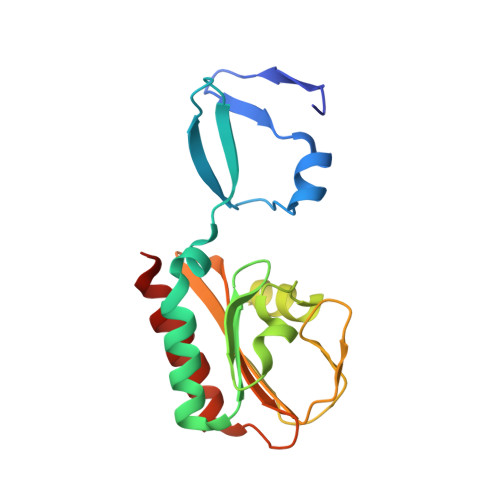
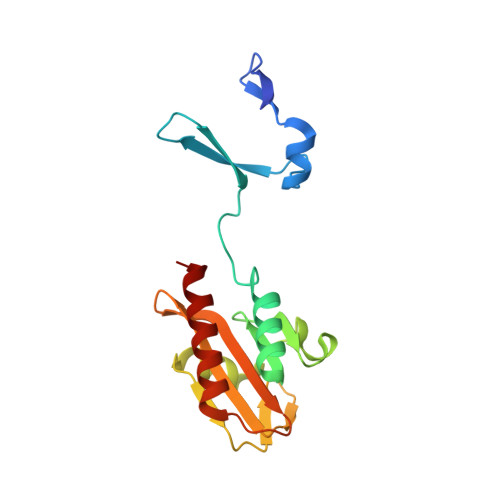
Crystal Structure of Spovt, the Final Modulator of Gene Expression During Spore Development in Bacillus Subtilis
Asen, I., Djuranovic, S., Lupas, A.N., Zeth, K.(2009) J Mol Biology 386: 962
- PubMed: 18996130
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.061
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2W1R, 2W1T - PubMed Abstract:
Endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis is orchestrated by five developmental sigma factors and further modulated by several auxiliary transcription factors. One of these, SpoVT, regulates forespore-specific sigma(G)-dependent genes and plays a key role in the final stages of spore formation. We have determined the crystal structure of the isolated C-terminal domain of SpoVT at 1.5 A by experimental phasing techniques and used this model to solve the structure of the full-length SpoVT at 2.6 A by molecular replacement. SpoVT is a tetramer that shows an overall significant distortion mediated by electrostatic interactions. Two monomers dimerize via the highly charged N-terminal domains to form swapped-hairpin beta-barrels. These asymmetric dimers further tetramerize through the formation of mixed helix bundles between their C-terminal domains, which themselves fold as GAF (cGMP-specific and cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterases, Anabaena adenylate cyclases, and Escherichia coli FhlA) domains. The combination of a swapped-hairpin beta-barrel with a GAF domain represents a novel domain architecture in transcription factors. The occurrence of SpoVT homologs throughout Bacilli and Clostridia demonstrates the ancestral origin of this factor in sporulation.
- Department of Membrane Biochemistry, Max Planck Institute for Biochemistry, Am Klopferspitz 18, 82152 Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: