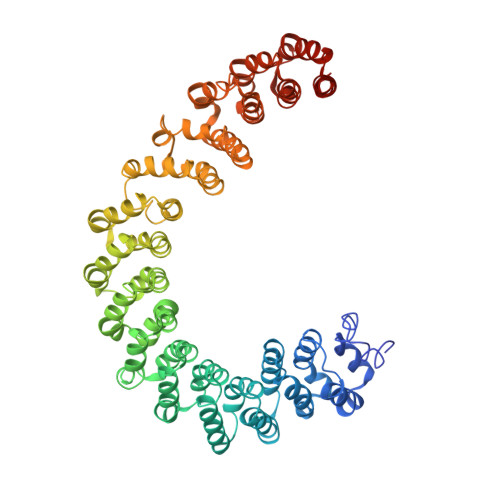
Structural basis of PP2A inhibition by small t antigen.
Cho, U.S., Morrone, S., Sablina, A.A., Arroyo, J.D., Hahn, W.C., Xu, W.(2007) PLoS Biol 5: e202-e202
- PubMed: 17608567
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050202
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PF4 - PubMed Abstract:
The SV40 small t antigen (ST) is a potent oncoprotein that perturbs the function of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). ST directly interacts with the PP2A scaffolding A subunit and alters PP2A activity by displacing regulatory B subunits from the A subunit. We have determined the crystal structure of full-length ST in complex with PP2A A subunit at 3.1 A resolution. ST consists of an N-terminal J domain and a C-terminal unique domain that contains two zinc-binding motifs. Both the J domain and second zinc-binding motif interact with the intra-HEAT-repeat loops of HEAT repeats 3-7 of the A subunit, which overlaps with the binding site of the PP2A B56 subunit. Intriguingly, the first zinc-binding motif is in a position that may allow it to directly interact with and inhibit the phosphatase activity of the PP2A catalytic C subunit. These observations provide a structural basis for understanding the oncogenic functions of ST.
- Department of Biological Structure, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: