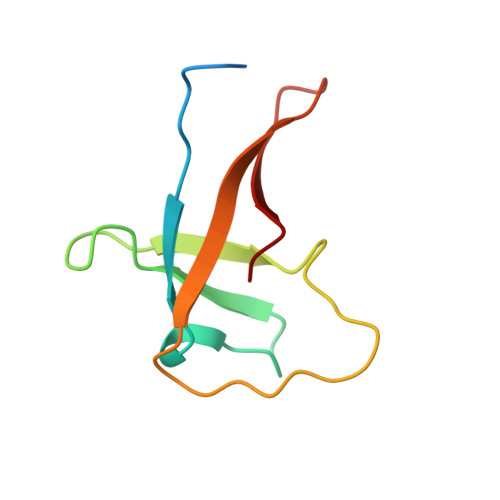
Solution structure of the RNA-binding cold-shock domain of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii NAB1 protein and insights into RNA recognition.
Sawyer, A.L., Landsberg, M.J., Ross, I.L., Kruse, O., Mobli, M., Hankamer, B.(2015) Biochem J 469: 97-106
- PubMed: 25919092
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20150217
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MQH - PubMed Abstract:
Light-harvesting complex (LHC) proteins are among the most abundant proteins on Earth and play critical roles in photosynthesis, both in light capture and in photoprotective mechanisms. The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii nucleic acid-binding protein 1 (NAB1) is a negative regulator of LHC protein translation. Its N-terminal cold-shock domain (CSD) binds to a 13-nt element [CSD consensus sequence (CSDCS)] found in the mRNA of specific LHC proteins associated with Photosystem II (PSII), an interaction which regulates LHC expression and, consequently, PSII-associated antenna size, structure and function. In the present study, we elucidated the solution structure of the NAB1 CSD as determined by heteronuclear NMR. The CSD adopts a characteristic five-stranded anti parallel β-barrel fold. Upon addition of CSDCS RNA, a large number of NMR chemical shift perturbations were observed, corresponding primarily to surface-exposed residues within the highly conserved β2- and β3-strands in the canonical RNA-binding region, but also to residues on β-strand 5 extending the positive surface patch and the overall RNA-binding site. Additional chemical shift perturbations that accompanied RNA binding involved buried residues, suggesting that transcript recognition is accompanied by conformational change. Our results indicate that NAB1 associates with RNA transcripts through a mechanism involving its CSD that is conserved with mechanisms of sequence-specific nucleic acid recognition employed by ancestrally related bacterial cold-shock proteins (CSPs).
- Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland 4072, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: