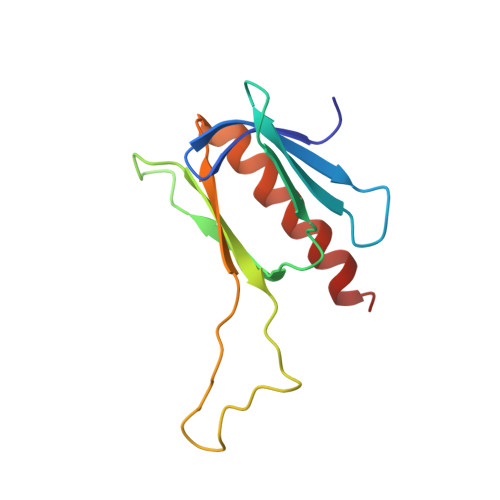
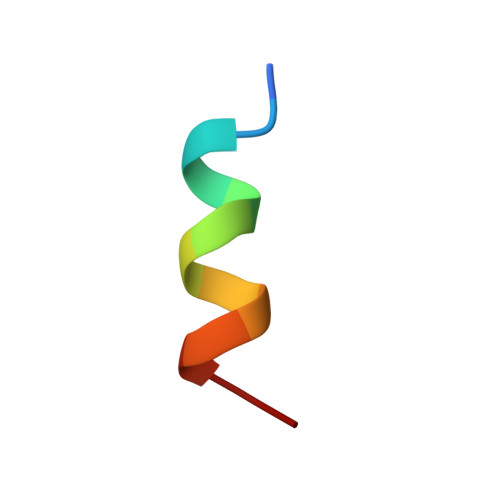
Structural and Functional Characterization of a Complex between the Acidic Transactivation Domain of EBNA2 and the Tfb1/p62 Subunit of TFIIH.
Chabot, P.R., Raiola, L., Lussier-Price, M., Morse, T., Arseneault, G., Archambault, J., Omichinski, J.G.(2014) PLoS Pathog 10: e1004042-e1004042
- PubMed: 24675874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004042
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MKR - PubMed Abstract:
Infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can lead to a number of human diseases including Hodgkin's and Burkitt's lymphomas. The development of these EBV-linked diseases is associated with the presence of nine viral latent proteins, including the nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2). The EBNA2 protein plays a crucial role in EBV infection through its ability to activate transcription of both host and viral genes. As part of this function, EBNA2 associates with several host transcriptional regulatory proteins, including the Tfb1/p62 (yeast/human) subunit of the general transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) and the histone acetyltransferase CBP(CREB-binding protein)/p300, through interactions with its C-terminal transactivation domain (TAD). In this manuscript, we examine the interaction of the acidic TAD of EBNA2 (residues 431-487) with the Tfb1/p62 subunit of TFIIH and CBP/p300 using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, isothermal titration calorimeter (ITC) and transactivation studies in yeast. NMR studies show that the TAD of EBNA2 binds to the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of Tfb1 (Tfb1PH) and that residues 448-471 (EBNA2₄₄₈₋₄₇₁) are necessary and sufficient for this interaction. NMR structural characterization of a Tfb1PH-EBNA2₄₄₈₋₄₇₁ complex demonstrates that the intrinsically disordered TAD of EBNA2 forms a 9-residue α-helix in complex with Tfb1PH. Within this helix, three hydrophobic amino acids (Trp458, Ile461 and Phe462) make a series of important interactions with Tfb1PH and their importance is validated in ITC and transactivation studies using mutants of EBNA2. In addition, NMR studies indicate that the same region of EBNA2 is also required for binding to the KIX domain of CBP/p300. This study provides an atomic level description of interactions involving the TAD of EBNA2 with target host proteins. In addition, comparison of the Tfb1PH-EBNA2₄₄₈₋₄₇₁ complex with structures of the TAD of p53 and VP16 bound to Tfb1PH highlights the versatility of intrinsically disordered acidic TADs in recognizing common target host proteins.
- Département de Biochimie et Médicine Moléculaire, Université de Montréal, Succursale Centre-Ville, Montréal, Québec, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: