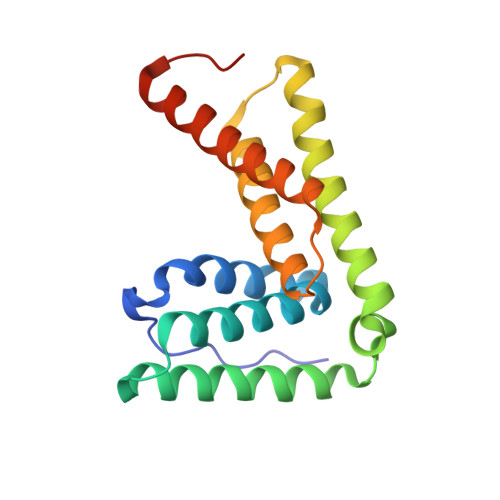
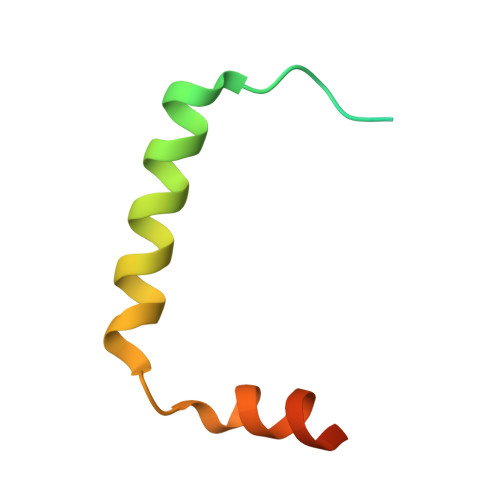
Interactions of the Human LIP5 Regulatory Protein with Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport.
Skalicky, J.J., Arii, J., Wenzel, D.M., Stubblefield, W.M., Katsuyama, A., Uter, N.T., Bajorek, M., Myszka, D.G., Sundquist, W.I.(2012) J Biological Chem 287: 43910-43926
- PubMed: 23105106
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.417899
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LXL, 2LXM - PubMed Abstract:
The endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) pathway remodels membranes during multivesicular body biogenesis, the abscission stage of cytokinesis, and enveloped virus budding. The ESCRT-III and VPS4 ATPase complexes catalyze the membrane fission events associated with these processes, and the LIP5 protein helps regulate their interactions by binding directly to a subset of ESCRT-III proteins and to VPS4. We have investigated the biochemical and structural basis for different LIP5-ligand interactions and show that the first microtubule-interacting and trafficking (MIT) module of the tandem LIP5 MIT domain binds CHMP1B (and other ESCRT-III proteins) through canonical type 1 MIT-interacting motif (MIM1) interactions. In contrast, the second LIP5 MIT module binds with unusually high affinity to a novel MIM element within the ESCRT-III protein CHMP5. A solution structure of the relevant LIP5-CHMP5 complex reveals that CHMP5 helices 5 and 6 and adjacent linkers form an amphipathic "leucine collar" that wraps almost completely around the second LIP5 MIT module but makes only limited contacts with the first MIT module. LIP5 binds MIM1-containing ESCRT-III proteins and CHMP5 and VPS4 ligands independently in vitro, but these interactions are coupled within cells because formation of stable VPS4 complexes with both LIP5 and CHMP5 requires LIP5 to bind both a MIM1-containing ESCRT-III protein and CHMP5. Our studies thus reveal how the tandem MIT domain of LIP5 binds different types of ESCRT-III proteins, promoting assembly of active VPS4 enzymes on the polymeric ESCRT-III substrate.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, Utah 84112-5650, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: