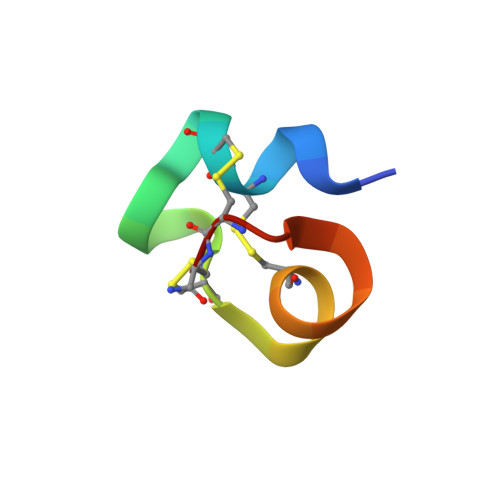
Mammalian neuronal sodium channel blocker mu-conotoxin BuIIIB has a structured N-terminus that influences potency.
Kuang, Z., Zhang, M.M., Gupta, K., Gajewiak, J., Gulyas, J., Balaram, P., Rivier, J.E., Olivera, B.M., Yoshikami, D., Bulaj, G., Norton, R.S.(2013) ACS Chem Biol 8: 1344-1351
- PubMed: 23557677
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb300674x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LO9, 2LOC - PubMed Abstract:
Among the μ-conotoxins that block vertebrate voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs), some have been shown to be potent analgesics following systemic administration in mice. We have determined the solution structure of a new representative of this family, μ-BuIIIB, and established its disulfide connectivities by direct mass spectrometric collision induced dissociation fragmentation of the peptide with disulfides intact. The major oxidative folding product adopts a 1-4/2-5/3-6 pattern with the following disulfide bridges: Cys5-Cys17, Cys6-Cys23, and Cys13-Cys24. The solution structure reveals that the unique N-terminal extension in μ-BuIIIB, which is also present in μ-BuIIIA and μ-BuIIIC but absent in other μ-conotoxins, forms part of a short α-helix encompassing Glu3 to Asn8. This helix is packed against the rest of the toxin and stabilized by the Cys5-Cys17 and Cys6-Cys23 disulfide bonds. As such, the side chain of Val1 is located close to the aromatic rings of Trp16 and His20, which are located on the canonical helix that displays several residues found to be essential for VGSC blockade in related μ-conotoxins. Mutations of residues 2 and 3 in the N-terminal extension enhanced the potency of μ-BuIIIB for NaV1.3. One analogue, [d-Ala2]BuIIIB, showed a 40-fold increase, making it the most potent peptide blocker of this channel characterized to date and thus a useful new tool with which to characterize this channel. On the basis of previous results for related μ-conotoxins, the dramatic effects of mutations at the N-terminus were unanticipated and suggest that further gains in potency might be achieved by additional modifications of this region.
- The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research , 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, Victoria, 3052, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: